What It Is
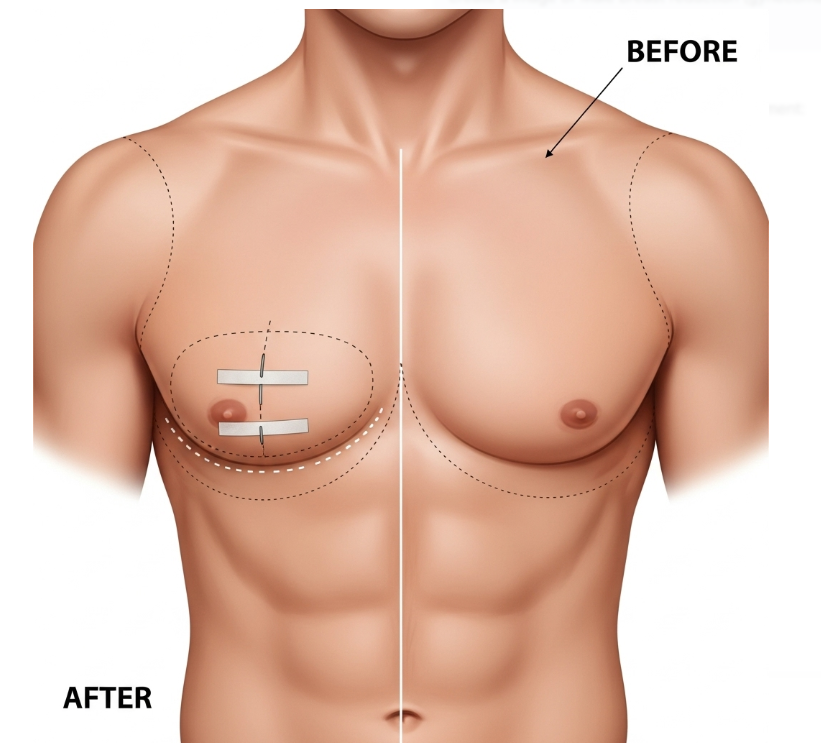
Male breast reduction, also known as gynecomastia surgery, is a procedure that removes excess glandular tissue, fat, and sometimes skin from the male chest to create a flatter, more masculine contour. Gynecomastia is a common condition that may result from hormonal imbalance, genetics, weight changes, medication side effects, or lifestyle factors.
In Korea, male breast reduction is performed with advanced methods such as liposuction, direct gland excision, or a combination of both, often leaving minimal scars. Korean surgeons focus on achieving a natural, athletic chest appearance with fast recovery and high precision.
Why It’s Done
Men undergo gynecomastia surgery because:
- Enlarged breasts cause embarrassment, low confidence, or discomfort.
- They experience difficulty wearing fitted clothing or going shirtless.
- Exercise and diet have not improved the condition.
- The enlargement is due to true glandular tissue (not just fat).
Good candidates include:
- Men with persistent gynecomastia not resolving with medical treatment or weight loss.
- Those in good physical health with stable weight.
- Patients with realistic expectations of results and scarring.
Alternatives
- Weight loss and exercise: May reduce fatty tissue but not glandular enlargement.
- Hormonal or medical treatment: For cases caused by endocrine issues.
- Non-surgical liposuction devices: Limited effect compared to surgery.
- Observation: In mild cases where appearance is not a concern.
Preparation
Before male breast reduction in Korea, patients will:
- Undergo a consultation including chest examination, hormone testing, and sometimes imaging (ultrasound or mammogram).
- Stop smoking and alcohol 2–4 weeks prior to surgery.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and certain supplements.
- Maintain stable weight and healthy lifestyle habits.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia depending on severity.
- Liposuction: Used to remove fatty tissue through small incisions.
- Gland excision: Performed through a small incision at the edge of the areola to remove firm glandular tissue.
- Skin tightening: In severe cases, excess skin is removed for chest contouring.
- Duration: 1–3 hours, usually outpatient.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort are common; compression garment worn to reduce swelling.
- Return to activities: Light activities in 3–5 days; strenuous exercise avoided for 4–6 weeks.
- Final results: Chest appears flatter and firmer within 1–2 months as swelling subsides.
Possible Complications
- Asymmetry or uneven contour.
- Visible scarring (usually hidden at the areola border).
- Temporary or permanent changes in nipple sensation.
- Hematoma or seroma (fluid buildup).
- Rare risks: infection or contour irregularities requiring revision.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons use physical examination, ultrasound, and hormone testing to determine the cause and severity of gynecomastia.
Medical Treatments
- Hormonal treatment for patients with underlying endocrine disorders.
- Weight management programs for those with obesity-related enlargement.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Liposuction-only reduction for fatty gynecomastia.
- Direct gland excision for firm glandular tissue.
- Combination technique (liposuction + excision) for best results.
- Skin excision and tightening for severe or long-standing gynecomastia.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Compression garments worn for 4–6 weeks.
- Scar care with silicone sheets or laser therapy.
- Long-term follow-up to monitor hormone balance and chest contour.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s refined surgical techniques, advanced liposuction technology, and discreet aftercare services.