What It Is
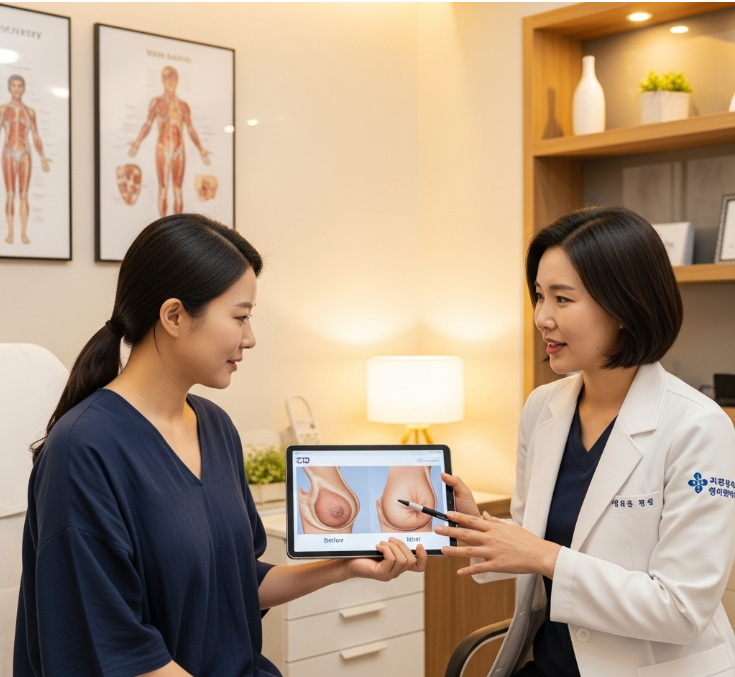
A breast lift, also called mastopexy, is a cosmetic surgical procedure that raises and reshapes sagging breasts by removing excess skin and tightening the surrounding tissues. Unlike breast augmentation, mastopexy focuses on lifting and contouring the existing breast tissue rather than increasing size (although it can be combined with implants or fat transfer for added volume).
In Korea, breast lifts are performed with advanced scar-minimizing techniques, 3D planning, and optional combination procedures to restore youthful, perky, and proportionate breasts.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo mastopexy because:
- Breasts sag after pregnancy, breastfeeding, weight loss, or aging.
- The nipples point downward or fall below the breast crease.
- The areolas have stretched and become enlarged.
- They want to restore a more youthful, uplifted appearance.
Good candidates include:
- Women in good health with realistic expectations.
- Patients with mild to severe breast ptosis (sagging).
- Those satisfied with breast size but unhappy with drooping.
Alternatives
- Breast implants: Add volume but do not significantly lift sagging tissue.
- Fat transfer: Subtle augmentation with mild lifting effect.
- Supportive bras or non-surgical treatments: Temporary cosmetic enhancement, but no long-term lift.
Preparation
Before breast lift surgery in Korea, patients will:
- Have a consultation with breast measurements and 3D simulations.
- Undergo breast imaging (mammogram or ultrasound if recommended).
- Stop smoking and alcohol 2–4 weeks prior.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and certain supplements.
- Plan recovery time away from strenuous activity.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is most common.
- Incisions: Type depends on degree of sagging:
- Periareolar (donut) for mild sagging.
- Vertical (lollipop) for moderate sagging.
- Anchor (inverted-T) for severe sagging.
- Reshaping: Excess skin is removed, breast tissue is lifted, and the nipple-areola complex is repositioned.
- Closure: Sutures are placed with attention to minimizing scars.
- Duration: 2–3 hours, usually outpatient.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and soreness are common; support bras are worn continuously.
- Stitches: Dissolvable or removed after 7–10 days.
- Return to activities: Light activity in 5–7 days; exercise avoided for 4–6 weeks.
- Final results: Breasts appear firmer, lifted, and more youthful within 2–3 months, with scars fading over 6–12 months.
Possible Complications
- Visible scarring or scar widening.
- Asymmetry between breasts.
- Temporary or permanent changes in nipple sensation.
- Infection or wound healing delays.
- Rare risks: poor blood supply to the nipple or skin.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons use 3D breast analysis, imaging, and detailed physical exam to determine the degree of ptosis and choose the most suitable technique.
Medical Treatments
- Support bras, skin tightening treatments, or fillers for very mild cases.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Periareolar mastopexy for mild sagging.
- Vertical mastopexy (lollipop) for moderate sagging.
- Anchor mastopexy (inverted-T) for severe sagging.
- Combination lift with implants or fat transfer for patients wanting both lift and volume.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Scar care with silicone gels, massage, or fractional laser.
- Long-term monitoring of breast health with imaging as needed.
- Lifestyle guidance to maintain results (stable weight, good skin care).
- International patients benefit from Korea’s breast surgery expertise, scar-minimizing techniques, and personalized aftercare.