What it is
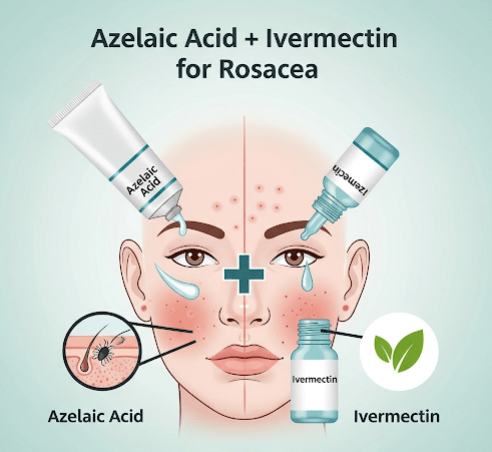
➝ Azelaic acid and ivermectin are two topical treatments commonly prescribed for rosacea, especially when used together as part of a combined management strategy.
➝ Azelaic acid (usually in 15% gel/foam or 20% cream) works as an anti-inflammatory and keratolytic agent. It reduces swelling, redness, and papules while also improving skin texture.
➝ Ivermectin (1% cream) is an anti-parasitic and anti-inflammatory medication. It targets Demodex mites, which are often more abundant in rosacea patients, and reduces skin inflammation.
➝ When used together, these two agents provide dual benefits:
- Azelaic acid reduces inflammation and pigmentation.
- Ivermectin addresses inflammation caused by Demodex and reduces papules and pustules.
Why it’s done
→ To treat papulopustular rosacea, characterized by bumps, pustules, and background redness.
→ To reduce persistent inflammation and improve skin barrier health.
→ To offer an effective non-antibiotic topical therapy, avoiding long-term oral antibiotics.
→ To manage rosacea safely in patients who cannot tolerate or prefer to avoid systemic treatments.
→ In Korea, dermatologists often recommend azelaic acid + ivermectin therapy as part of a stepwise approach, starting with topicals before considering oral doxycycline or laser treatments.
Alternatives
→ Other topical treatments:
- Metronidazole cream or gel.
- Brimonidine or oxymetazoline cream (for redness only).
- Sulfur-based washes.
→ Oral treatments:
- Low-dose doxycycline (anti-inflammatory dose).
- Minocycline or isotretinoin (for resistant cases).
→ Laser and light-based therapies:
- Intense Pulsed Light (IPL).
- Pulsed Dye Laser (PDL).
- Nd:YAG laser for persistent redness and visible vessels.
→ Lifestyle measures: Avoiding triggers (alcohol, spicy food, extreme temperature, stress).
Preparation
→ Dermatologist consultation to confirm rosacea type and severity.
→ Patients are advised to:
- Start slowly (every other day) with azelaic acid to minimize irritation.
- Apply ivermectin once daily, usually at night.
- Use gentle cleansers and moisturizers to support skin barrier.
- Avoid harsh exfoliants and alcohol-based skincare products.
→ In Korea, patients often receive skincare counseling along with prescriptions to ensure compliance and minimize irritation.
How it’s Done
→ Azelaic acid is applied once or twice daily in a thin layer on affected areas.
→ Ivermectin is applied once daily (usually at night), covering the entire affected area.
→ The two can be alternated (morning and evening) or layered, depending on tolerance and dermatologist guidance.
→ Combination therapy is often continued for 12–16 weeks, with long-term maintenance as needed.
→ In Korean clinics, dermatologists sometimes pair these topicals with procedural treatments (IPL, PDL) for maximum results.
Recovery
→ Early improvement (less burning, fewer bumps) is often seen within 3–4 weeks.
→ Significant reduction in papules, pustules, and background redness usually occurs by 8–12 weeks.
→ Skin texture becomes smoother, and patients often notice fewer flare-ups over time.
→ With consistent use and avoidance of triggers, many patients maintain long-term control without requiring oral medications.
Complications
→ Azelaic acid may cause mild stinging, burning, or dryness at the beginning.
→ Ivermectin is generally well tolerated, but some patients may experience mild itching or skin irritation.
→ Both treatments are considered safe for long-term use and do not carry the systemic risks of oral medications.
→ Rare cases of hypersensitivity may occur, requiring discontinuation.
Treatment Options in Korea
→ Widely used in dermatology clinics and aesthetic centers as part of rosacea management.
→ Korean dermatologists often prescribe azelaic acid in the morning and ivermectin in the evening, combined with gentle K-beauty moisturizers to reduce irritation.
→ Clinics may integrate topical therapy with laser treatments (IPL, PDL, Nd:YAG) for persistent redness and visible blood vessels.
→ Patient education is a priority: Korean doctors often provide step-by-step skincare routines, teaching patients how to apply products in the correct sequence for best results.
→ This combination is highly valued in Korea for its dual mechanism, allowing patients to control inflammatory rosacea effectively without relying on long-term antibiotics.