What It Is
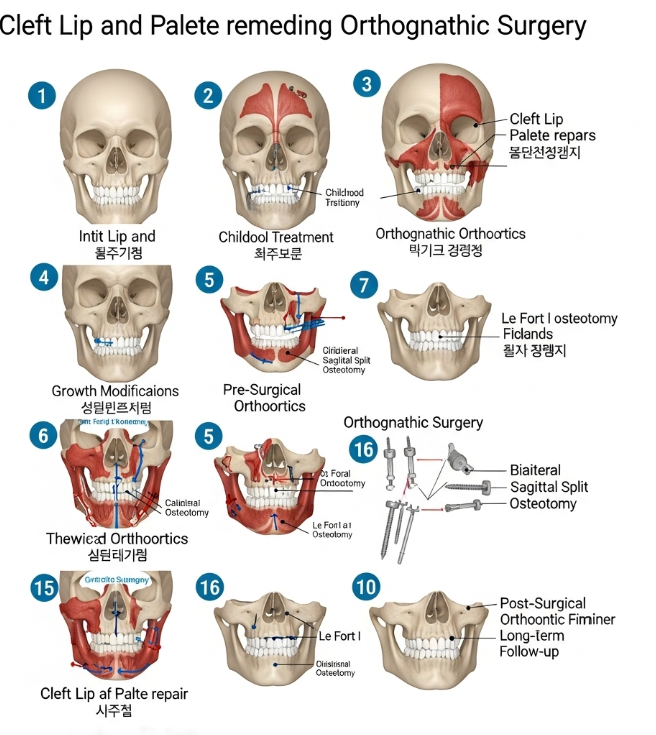
Orthognathic surgery cleft sequence refers to the series of jaw surgeries performed in patients with a history of cleft lip and/or palate to correct skeletal deformities, malocclusion (misaligned bite), and facial asymmetry. Cleft patients often develop growth disturbances of the upper jaw (maxilla), leading to underdevelopment, misalignment with the lower jaw, and difficulties in chewing, speaking, and facial aesthetics.
The cleft sequence typically includes Le Fort I osteotomy for advancing the maxilla, sometimes combined with mandibular surgery (bilateral sagittal split osteotomy, BSSO) for optimal bite alignment. In Korea, orthognathic surgery is performed using 3D virtual planning, custom plates, and advanced orthodontic coordination, ensuring functional correction and improved facial harmony.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo orthognathic surgery in the cleft sequence because:
- They have jaw misalignment (often underbite or crossbite).
- Chewing, speech, and airway function are compromised.
- Facial asymmetry affects self-confidence and appearance.
- Orthodontic treatment alone cannot correct severe skeletal discrepancies.
Good candidates include:
- Adolescents and adults with completed jaw growth (usually 16–18 years or older).
- Cleft patients with functional problems such as difficulty chewing, speech issues, or obstructive airway.
- Those in good health able to undergo major surgery.
Alternatives
- Orthodontics alone: Works for mild cases but not for skeletal deformities.
- Distraction osteogenesis: In some younger patients, bone is gradually lengthened to advance the maxilla.
- Prosthetics or cosmetic camouflage: Improves appearance but not function.
Preparation
Before orthognathic surgery in Korea, patients will:
- Undergo comprehensive orthodontic treatment to align teeth in preparation for surgery.
- Have 3D CT scans and dental models for surgical planning.
- Receive evaluation from a multidisciplinary team (plastic surgeon, orthodontist, ENT, speech therapist).
- Stop smoking and alcohol 4 weeks before surgery.
- Avoid medications that increase bleeding risk.
How It’s Done
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia is required.
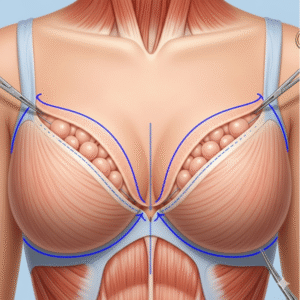
- Incisions: Made inside the mouth to avoid visible scars.
- Bone repositioning:
- Le Fort I osteotomy: The maxilla is mobilized and moved forward or repositioned.
- BSSO (mandibular surgery): Performed if lower jaw adjustment is needed.
- Fixation: Titanium plates and screws secure the bones in their new position.
- Additional refinements: Rhinoplasty or lip revision may be combined in cleft patients.
- Duration: 3–6 hours depending on complexity.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild pain are common. Patients follow a liquid or soft diet.
- Hospital stay: Typically 5–7 days.
- Diet: Gradual transition from liquid to soft foods over 4–6 weeks.
- Return to activities: Light activities after 2 weeks; full recovery in 2–3 months.
- Final results: Improved bite, speech, airway function, and facial aesthetics within 6–12 months.
Possible Complications
- Numbness in lips or cheeks due to nerve stretching (may be temporary or permanent).
- Infection or delayed healing at osteotomy sites.
- Relapse or minor movement of jaw position.
- Malocclusion requiring orthodontic refinement.
- Rare risks: airway obstruction, scarring inside the mouth.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean cleft teams use 3D CT imaging, digital dental scans, cephalometric analysis, and virtual surgical planning to design the sequence of surgeries.
Medical Treatments
- Orthodontic treatment before and after surgery.
- Speech therapy and ENT care for associated cleft-related issues.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Le Fort I osteotomy for maxillary advancement.
- BSSO for mandibular repositioning if required.
- Segmental osteotomy for dental arch correction.
- Distraction osteogenesis in selected growing patients.
- Combined cleft revisions (lip, nose, alveolar graft) coordinated with jaw surgery.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Long-term orthodontic management after surgery.
- Scar management for prior cleft surgeries.
- Speech therapy for articulation improvement.
- International patients benefit from Korea’s multidisciplinary cleft centers, 3D-guided orthognathic techniques, and comprehensive aftercare support.