What it is
Fractional tattoo assist in Korea is an advanced technique that combines fractional laser treatment with standard tattoo removal lasers.
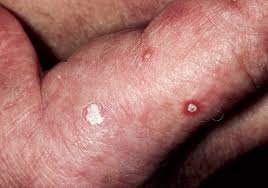
Traditional tattoo removal lasers (such as Pico or Q-switched Nd:YAG) break down pigment particles, but stubborn ink—especially deep-set pigments or resistant colors—may remain. Fractional laser technology works by creating microscopic treatment zones in the skin, stimulating collagen remodeling and improving skin healing.
→ When used as an “assist” in tattoo removal, fractional lasers help:
- Loosen remaining pigment that is trapped in scar tissue or deep skin layers.
- Smooth skin texture where tattoos have caused scarring.
- Enhance pigment clearance by improving skin permeability for subsequent laser passes.
• In Korea, fractional tattoo assist is often used for difficult tattoos that have not responded well to conventional methods, or for patients seeking both pigment clearance and smoother skin recovery.
Why it’s done
Patients in Korea undergo fractional tattoo assist treatments for several reasons:
→ Stubborn ink: Tattoos that remain after many sessions of standard laser treatment.
→ Scarred tattoo areas: Tattoos sometimes create raised or textured skin; fractional lasers help remodel this tissue.
→ Faster fading: Combining fractional laser with pigment-targeting lasers accelerates results.
→ Improved cosmetic outcome: Not only removing ink but also improving the skin’s appearance and smoothness.
→ Cover-up preparation: Some clients want smoother, lighter tattoo areas to prepare for new designs.
Alternatives
Other methods to improve stubborn tattoo removal include:
• Standard Pico or Q-switched lasers → Effective for most tattoos, but less so for resistant pigments or scarred tissue.
• R20 or R0 protocols → Multiple laser passes in one session for deeper fading.
• Surgical excision → Cutting out the tattooed skin; used only for small tattoos due to scarring.
• Dermabrasion → Mechanical removal of skin layers; outdated and risky.
→ Compared to these, fractional tattoo assist in Korea uniquely addresses both pigment removal and skin quality restoration, which is why it is becoming more popular.
Preparation
Before undergoing fractional tattoo assist in Korea, preparation is essential:
- Consultation → A dermatologist assesses tattoo color, depth, and any skin scarring.
- Skin evaluation → Because fractional lasers target skin structure, conditions like eczema or psoriasis must be ruled out.
- Avoid sun exposure → No tanning for at least 2–3 weeks before treatment.
- Stop irritants → Retinoids, acids, and exfoliants should be discontinued around the treatment area.
- Medical history → Patients with a history of keloid scarring are evaluated carefully.
→ Clinics in Korea often apply topical numbing cream before the procedure, as fractional lasers can be more uncomfortable than pigment-targeting lasers alone.
How it’s done
Fractional tattoo assist in Korea involves a two-step or combined approach:
- Fractional laser treatment
- A fractional CO₂ or Er:YAG laser is applied first.
- The laser creates microscopic channels in the skin, breaking scar tissue and stimulating healing.
- This process allows better access for pigment-targeting lasers.
- Pigment laser application
- After fractional treatment, a Pico or Q-switched laser is used to break down tattoo pigments.
- Because the skin has been pretreated, the pigment is more responsive to the laser energy.
- Cooling and soothing
- The treated area is cooled with ice packs or air blowers.
- Healing ointments are applied to minimize irritation.
→ A session lasts 30–60 minutes depending on tattoo size and complexity.
→ Patients typically need 4–8 sessions, spaced 6–8 weeks apart, though stubborn tattoos may require more.
Recovery
Recovery after fractional tattoo assist in Korea can be slightly longer than standard laser tattoo removal due to deeper skin involvement:
• Redness and swelling → Usually lasts a few days, more noticeable than with pigment-only lasers.
• Microscopic crusting or scabbing → A natural part of fractional healing, typically resolving within 5–7 days.
• Dryness or flaking → Common for about a week; moisturizing ointments are recommended.
• Sun protection → Strong SPF is mandatory to prevent hyperpigmentation.
• Avoid irritation → Patients must avoid saunas, sweating, or harsh skincare for at least one week.
→ Despite a slightly longer recovery, the benefit is improved skin texture along with tattoo fading.
Complication
Possible risks of fractional tattoo assist include:
- Hyperpigmentation → Darkening of skin, particularly in darker skin types.
- Hypopigmentation → Lightened patches where pigment is lost.
- Prolonged redness → May last longer than with single laser methods.
- Scarring → Rare, but possible if aftercare is neglected.
- Incomplete removal → Resistant pigments (like yellow or green) may remain despite combination therapy.
→ Korean dermatologists carefully balance laser settings to minimize these risks, making the procedure safer and more effective.
Treatment option in Korea
Korea is well-known for its innovative approaches in dermatology, and fractional tattoo assist is offered at many high-end clinics:
→ Advanced equipment → Fractional CO₂ and Er:YAG lasers are often combined with PicoSure, PicoWay, or Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers.
→ Expertise → Korean specialists are skilled in adjusting laser wavelengths, energy levels, and fractional depths based on tattoo type and skin condition.
• Combination treatments → Clinics often combine fractional assist with post-care therapies like LED healing, regenerative serums, or soothing hydrogel packs.
• Medical tourism → International patients come to Korea for difficult tattoo removals, especially when previous attempts abroad have failed.
• Aesthetic focus → Beyond pigment clearance, Korean clinics emphasize overall skin health and cosmetic appearance, ensuring smoother, clearer results.
→ With a reputation for precision and innovation, fractional tattoo assist in Korea is considered one of the best options for removing stubborn tattoos while simultaneously rejuvenating the skin.