What it is
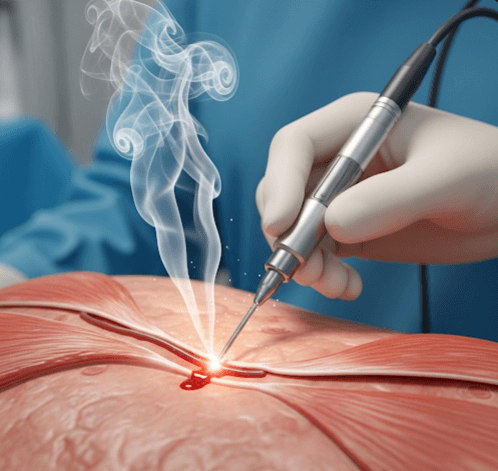
Electrosurgery hemostasis in Korea is a medical technique that uses high-frequency electrical current to stop bleeding during surgical or dermatological procedures.
By applying controlled electrical energy through a fine electrode, blood vessels are coagulated (sealed), preventing further bleeding. This makes the surgical field clearer and reduces the risk of complications.
→ In Korean dermatology and surgical clinics, electrosurgery is a standard adjunct technique used in procedures such as mole removal, skin cancer excision, biopsies, cosmetic surgery, and ENT operations.
• Electrosurgery is valued for its precision, speed, and reduced need for suturing.
• It is particularly useful for small vessels and capillaries.
Why it’s done
Patients in Korea benefit from electrosurgical hemostasis for multiple reasons:
→ Bleeding control → Ensures a clear operative field for accuracy.
→ Reduced risk of infection → By sealing vessels, bacterial entry is minimized.
→ Shorter surgery time → Less bleeding means quicker procedures.
→ Cosmetic refinement → Preserves surrounding tissue, which is vital in Korea’s aesthetics-focused medical field.
→ Versatility → Used in dermatology, cosmetic, ENT, and gynecology procedures.
Alternatives
Other methods of achieving hemostasis include:
• Manual pressure → Simple but less precise.
• Chemical cautery → Silver nitrate sticks used for small vessel bleeding.
• Cryotherapy → Freezing blood vessels, less common in surgical settings.
• Sutures or ligation → Mechanical tying of blood vessels.
• Laser coagulation → Uses light energy instead of electricity.
→ Electrosurgery is preferred for efficiency, precision, and minimal trauma to surrounding tissue.
Preparation
Before undergoing a procedure that uses electrosurgical hemostasis in Korea, preparation includes:
- Patient evaluation → Review of bleeding history and medications (e.g., blood thinners).
- Device setup → Electrosurgical unit calibrated to safe power settings.
- Sterile precautions → Standard surgical field preparation.
- Anesthesia → Local anesthesia is usually applied for patient comfort.
- Grounding pad application → For monopolar electrosurgery, a grounding pad is placed to safely disperse electrical current.
→ Korean hospitals follow international safety protocols for electrosurgical devices.
How it’s done
Electrosurgery hemostasis in Korea is performed step by step:
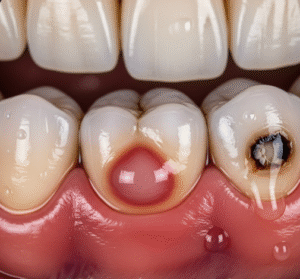
- Exposure of bleeding site → The surgeon identifies the vessel.
- Application of electrode → A fine probe delivers high-frequency current directly to the vessel.
- Coagulation → Heat seals the vessel walls, stopping bleeding.
- Repeat as necessary → Multiple points may be treated if bleeding persists.
- Completion of procedure → Hemostasis allows the surgery to proceed or finish cleanly.
→ Depending on the procedure, monopolar or bipolar electrosurgery may be used:
- Monopolar → For larger fields, requires grounding pad.
- Bipolar → Safer for delicate areas, current passes only between tweezer-like electrodes.
Recovery
Recovery after electrosurgery hemostasis is typically smooth:
• Immediate effect → Bleeding stops during surgery itself.
• Minimal tissue trauma → Precise application reduces collateral damage.
• Wound healing → Comparable to standard surgical wounds, healing within 1–3 weeks.
• Aftercare → Ointment or dressings may be applied depending on procedure.
• Scar outcome → Usually minimal, though pigmentation changes may occur temporarily.
→ Patients can resume normal activities depending on the overall surgery performed.
Complication
While generally safe, possible complications include:
- Thermal damage → Overheating may affect surrounding tissues if not carefully controlled.
- Pigment changes → Hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation at the site.
- Scarring → Rare, but possible with repeated or deep coagulation.
- Recurrence of bleeding → If vessel sealing is incomplete.
- Electrical risks → Extremely rare in modern Korean hospitals with strict safety protocols.
→ Risks are minimized in Korea due to highly trained surgeons and advanced electrosurgical systems.
Treatment option in Korea
Korea offers highly advanced electrosurgery hemostasis systems across medical fields:
→ Dermatology and cosmetic surgery → Used in mole removal, wart excision, biopsies, and minor skin surgeries.
→ ENT and oral surgery → Applied during tonsillectomy, nasal polyp removal, or oral lesion excision.
• Plastic surgery clinics → Combine hemostasis with aesthetic reconstruction for minimal scarring.
• Cutting-edge devices → Korean hospitals use the latest monopolar and bipolar electrosurgical units with safety monitoring.
• Integrated care → Often paired with laser or radiofrequency systems for dual precision.
→ With its combination of advanced technology, surgical expertise, and aesthetic awareness, electrosurgery hemostasis in Korea ensures safe, efficient, and cosmetically refined bleeding control during medical and cosmetic procedures.