What it is
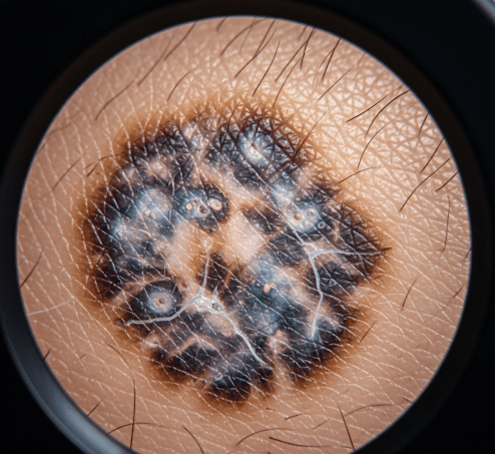
Dermatoscopic triage (dermatoscopy) in Korea is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that uses a dermatoscope (a handheld magnifying device with polarized or non-polarized light) to examine skin lesions in detail.
It allows dermatologists to visualize subsurface skin structures not visible to the naked eye, helping distinguish between benign lesions, precancerous changes, and malignant skin cancers.
→ “Triage” in this context means using dermatoscopy to decide whether a lesion requires monitoring, biopsy, or immediate removal.
• Widely used in dermatology clinics, skin cancer centers, and plastic surgery hospitals across Korea.
• Considered the gold standard for early detection of melanoma and other pigmented lesions.
Why it’s done
Patients in Korea undergo dermatoscopic triage for:
→ Early melanoma detection → Dermatoscopy can detect features invisible to the naked eye.
→ Screening suspicious moles → Especially when there are many pigmented lesions.
→ Differentiating benign vs malignant growths → Reduces unnecessary biopsies.
→ Monitoring skin changes → Regular dermatoscopic imaging helps track mole evolution.
→ Cosmetic decision-making → Assists in identifying safe lesions for cosmetic removal.
Alternatives
Other diagnostic methods include:
• Naked-eye clinical exam → Less accurate, higher chance of missed melanoma.
• Biopsy (shave, punch, excisional) → Definitive but invasive.
• Confocal microscopy → Advanced imaging, not widely available.
• Mole mapping (digital total body photography) → Tracks mole changes over time.
→ Dermatoscopy is preferred as the first-line triage tool, balancing accuracy with non-invasiveness.
Preparation
Before dermatoscopic triage in Korea, preparation is minimal:
- Patient history → Includes family history of melanoma, sun exposure habits, and lesion changes.
- Skin inspection → Full-body or localized exam, depending on patient concern.
- Photography setup → Clinics often use digital dermatoscopes with imaging software.
- No special restrictions → Patients don’t need to stop skincare products or medications.
→ Korean clinics emphasize preventive skin checks, often recommending annual dermatoscopic exams for high-risk individuals.
How it’s done
Dermatoscopic triage in Korea is a quick, painless process:
- Visual inspection → Dermatologist examines the lesion with the naked eye.
- Dermatoscope application
- Polarized or non-polarized light used to see deeper structures.
- Magnification (10x–20x) reveals pigment networks, vascular patterns, and lesion symmetry.
- Pattern analysis → Lesion is evaluated using algorithms (e.g., ABCD rule, 7-point checklist, or pattern analysis).
- Decision-making
- Benign → Reassurance or optional removal.
- Suspicious → Biopsy or excision recommended.
- Indeterminate → Digital monitoring for changes.
→ The procedure takes 5–20 minutes, depending on the number of lesions examined.
Recovery
Dermatoscopic triage has no downtime:
• Non-invasive → No cutting, bleeding, or anesthesia required.
• Immediate results → Dermatologist gives recommendations during the visit.
• Follow-up → Some lesions may be photographed and reviewed over months or years.
→ Patients can resume normal activities immediately.
Complication
Dermatoscopy itself is safe, but limitations include:
- False negatives → Rare, but very early melanoma may resemble benign lesions.
- False positives → May lead to unnecessary biopsy.
- Operator dependency → Accuracy depends on dermatologist’s skill and experience.
- Monitoring fatigue → Patients with many moles require frequent checks.
→ In Korea, risks are minimized due to dermatologists’ advanced training and use of digital dermoscopy systems.
Treatment option in Korea
Korea is highly advanced in dermatoscopic triage and skin cancer detection:
→ Dermatology clinics → Widely equipped with dermatoscopes for routine mole checks.
→ Digital dermoscopy systems → Many clinics use mole-mapping technology for photographic tracking.
• Early detection programs → Preventive skin cancer screening is emphasized in Korean healthcare.
• Integration with pathology → Suspicious lesions are biopsied in the same clinic for fast results.
• Medical tourism → Patients visit Korea for comprehensive mole checks, combining oncologic accuracy with cosmetic decision-making.
→ With its precision imaging, skilled dermatologists, and emphasis on early intervention, dermatoscopic triage in Korea is one of the most effective approaches to skin lesion evaluation worldwide.