What It Is
A rotation flap is a local reconstructive surgery technique in which adjacent skin and soft tissue are rotated in an arc-shaped fashion to cover a nearby wound or defect. Unlike an advancement flap that moves tissue straight forward, the rotation flap uses a curved incision to swing skin into place, allowing for coverage of larger or irregularly shaped defects while maintaining good blood supply.
This procedure is often performed after tumor excision (such as Mohs surgery), trauma injuries, scar contracture release, or congenital defect repair, especially in cosmetically and functionally sensitive areas like the face, scalp, and trunk.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo rotation flap surgery because:
- They have a defect that cannot be closed with simple sutures or grafts.
- They want a natural skin match in color, texture, and thickness.
- They have irregularly shaped wounds where straight-line closure is not possible.
- The defect is located in a highly visible area where cosmetic outcome is important.
Good candidates include:
- Patients with medium to large wounds surrounded by healthy, elastic skin.
- Individuals with defects in curved or mobile regions like the face, cheek, or scalp.
- People in good general health without local infection.
Alternatives
- Advancement flap: Better for smaller, straight-line defects.
- Transposition flap (e.g., Z-plasty, bilobed flap): Used when tissue must be shifted over intervening skin.
- Skin grafts: Suitable for large areas but may not blend naturally.
- Free flaps: Used for very large or complex wounds where local tissue is insufficient.
Preparation
Before undergoing rotation flap surgery in Korea, patients will:
- Have a consultation with a reconstructive surgeon, including evaluation of defect size, skin elasticity, and flap design.
- Undergo standard medical testing (bloodwork, imaging if required).
- Stop smoking and alcohol 2–4 weeks before surgery to preserve vascular supply.
- Avoid blood-thinning medications and certain supplements.
- Discuss expected scar patterns, as the incision is longer than the defect itself.
How It’s Done
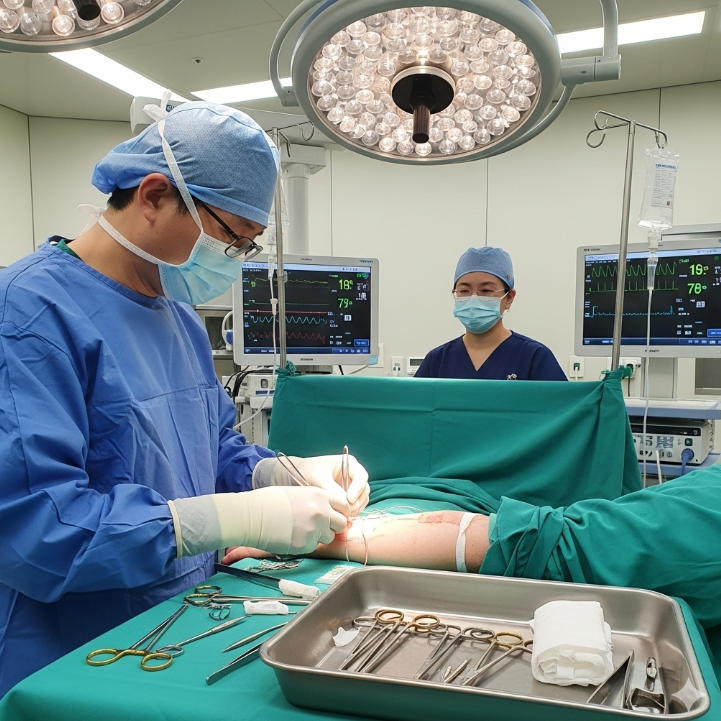
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia depending on defect size and location.
- Flap design: The surgeon marks a curved, arc-like incision adjacent to the defect.
- Flap elevation: The tissue is lifted carefully, maintaining its vascular connection.
- Rotation: The flap is rotated into the defect and sutured in place.
- Closure: The donor site is closed with fine sutures to minimize scarring.
- Duration: 1–3 hours depending on complexity.
Recovery
- First week: Swelling, bruising, and mild discomfort are expected. Sutures are usually removed within 5–14 days.
- Return to activities: Most patients resume light activities within a week.
- Healing: The flap is monitored closely to ensure blood supply remains intact.
- Final results: Natural blending of skin texture and color typically occurs within 2–3 months, with scars continuing to refine over time.
Possible Complications
- Partial flap loss due to compromised blood flow.
- Temporary numbness or tightness in the treated area.
- Longer scars due to the curved incision design.
- Rare risks: infection, wound reopening, or asymmetry.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean surgeons evaluate the wound and surrounding skin with 3D planning tools and dermoscopy when needed, ensuring precise flap design and optimal cosmetic outcome.
Medical Treatments
For smaller defects, alternatives such as direct closure, laser resurfacing, or skin grafting may be considered.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Rotation flap for medium to large irregular defects.
- Multiple flap combinations (rotation plus advancement or Z-plasty) for complex reconstructions.
- Use of microsurgical refinement techniques to optimize blood supply and minimize scarring.
Rehabilitation and Support
- Regular follow-up visits to ensure flap survival and wound healing.
- Scar management treatments (silicone sheets, fractional CO₂ laser, microneedling).
- Physiotherapy when rotation flaps are near joints to restore mobility.
- International clinics in Korea provide multilingual aftercare services and detailed recovery instructions.