Overview
Vaginal bleeding refers to any bleeding from the vagina, including normal menstrual bleeding and abnormal bleeding outside of the menstrual cycle. While it can be a normal part of reproductive health, abnormal vaginal bleeding may signal an underlying medical condition and warrants proper evaluation, especially in postmenopausal women or during pregnancy.
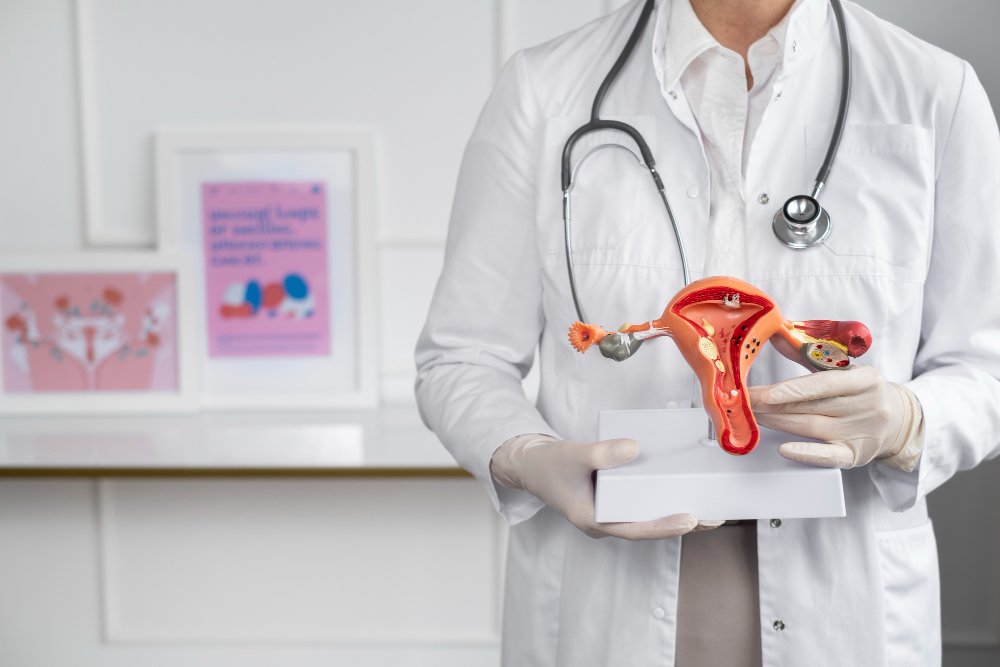
What is Vaginal Bleeding
Vaginal Bleeding is defined as blood loss originating from the vaginal canal, whether associated with menstruation or not. It may be categorized as:
- Menstrual bleeding: Normal monthly periods
- Intermenstrual bleeding: Between periods
- Postcoital bleeding: After sexual intercourse
- Postmenopausal bleeding: After menopause
- Breakthrough bleeding: While using hormonal contraception
Abnormal vaginal bleeding can result from hormonal imbalances, structural problems in reproductive organs, infections, or serious conditions like cancer or pregnancy complications.
Symptoms
Vaginal bleeding may present with various symptoms, depending on its cause:
- Bleeding between menstrual periods
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia)
- Spotting or light bleeding outside normal periods
- Bleeding after sex
- Bleeding after menopause
- Pelvic or abdominal pain
- Passage of large blood clots
- Fatigue or dizziness (due to blood loss)
In pregnancy, vaginal bleeding may be a sign of a complication and should be treated urgently.
Causes
Causes of vaginal bleeding differ by age and hormonal status:
In reproductive-age women:
- Hormonal imbalances (e.g., thyroid disorders, PCOS)
- Uterine fibroids or polyps
- Endometriosis or adenomyosis
- Ovulation-related spotting
- Miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic infections (e.g., STIs)
In postmenopausal women:
- Endometrial or cervical cancer
- Endometrial atrophy
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Vaginal dryness or trauma
Other possible causes:
- Medications (e.g., anticoagulants)
- Birth control pills or IUDs
- Bleeding disorders
Risk Factors
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Use of hormonal contraceptives
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Menopause or perimenopause
- Pregnancy or recent miscarriage
- Uterine or cervical abnormalities
- History of reproductive cancers
- Sexually transmitted infections
Complications
Untreated or severe vaginal bleeding can lead to:
- Anemia (low red blood cell count)
- Severe blood loss and shock (in acute cases)
- Infertility or miscarriage
- Progression of undiagnosed cancers
- Emotional distress or sexual dysfunction
- Chronic pain or pelvic discomfort
Prevention
While not all causes can be prevented, some measures can help:
- Maintain a regular menstrual calendar to detect abnormalities
- Use contraception as prescribed and attend follow-ups
- Manage chronic conditions, such as PCOS or thyroid disease
- Practice safe sex to avoid STIs
- Avoid overuse of hormone medications without medical guidance
- Regular gynecologic exams, especially after menopause
Treatment Options in Korea
South Korea offers comprehensive diagnostic tools and individualized care for women experiencing vaginal bleeding. The focus is on accurate diagnosis, minimally invasive procedures, and fertility preservation when needed.
- Diagnostic services:
- Pelvic exam and Pap smear
- Transvaginal ultrasound or pelvic MRI
- Endometrial biopsy
- Hormonal blood tests
- Pregnancy test (to rule out miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy)
- Treatment options:
- Hormonal therapy (e.g., oral contraceptives, progesterone)
- Antibiotics for infections
- Surgical options:
- Polypectomy or fibroid removal (hysteroscopic or laparoscopic)
- Dilation and curettage (D&C)
- Endometrial ablation
- Hysterectomy (in severe or cancer-related cases)
- Iron supplements or transfusion for blood loss
- Cancer treatment, if indicated
South Korea’s hospitals offer cutting-edge imaging, expert gynecologists, and advanced surgical options, making it a top destination for diagnosis and management of abnormal vaginal bleeding.