What It Is
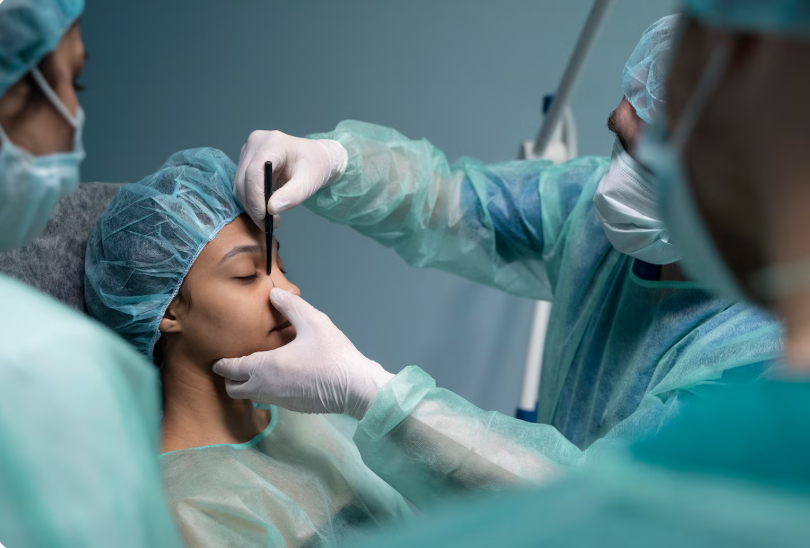
Septoplasty is a surgical procedure aimed at correcting a deviated nasal septum—the cartilage and bone dividing the two nasal cavities. A deviated septum can cause nasal obstruction, chronic sinusitis, snoring, and difficulty breathing. Septoplasty realigns or removes the obstructing portions of the septum while preserving structural support and nasal function.
Why It’s Done
Patients undergo septoplasty to:
- Improve airflow through the nasal passages
- Reduce nasal congestion and sinus infections
- Alleviate snoring or sleep-disordered breathing
- Correct structural issues from trauma or congenital deformities
This procedure is commonly chosen by adults with chronic nasal obstruction, sometimes in combination with turbinate reduction or rhinoplasty for functional and aesthetic improvement.
Alternatives
Non-surgical alternatives include:
- Nasal corticosteroid sprays to reduce inflammation
- Antihistamines for allergy-related congestion
- Nasal dilators or splints to improve airflow temporarily
However, these measures do not correct the underlying structural problem.
Preparation
Preparation includes:
- Comprehensive nasal examination and imaging (e.g., CT scan if needed)
- Assessment for allergies or sinus disease contributing to obstruction
- Avoiding blood-thinning medications and smoking
- Fasting if general anesthesia is planned
How It’s Done
Septoplasty is performed under local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia. Steps include:
- Incisions are made inside the nasal cavity to access the septum
- Deviated cartilage and/or bone is repositioned or removed
- Nasal mucosa is preserved as much as possible to promote healing
- Splints or packing may be placed temporarily to support the septum
The procedure usually takes 1–2 hours and is typically outpatient.
Recovery
Recovery involves:
- Mild swelling, nasal congestion, and discomfort for several days
- Avoiding nose blowing, heavy lifting, or trauma to the nose
- Saline irrigations and follow-up visits to monitor healing
- Most patients return to normal activities within 1–2 weeks, with full improvement in breathing over several weeks
Possible Complications
Potential risks include:
- Bleeding or infection
- Septal perforation (rare)
- Persistent obstruction if correction is incomplete
- Changes in nasal shape or asymmetry
Experienced surgeons in Korea minimize these risks and ensure functional and aesthetic outcomes.
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
Korean ENT specialists evaluate septal deviation through physical examination, nasal endoscopy, and imaging to determine severity and plan surgery.
Medical Treatments
Non-surgical management includes corticosteroid sprays, antihistamines, decongestants, and allergy therapy to manage symptoms temporarily.
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
Advanced techniques in Korea include endoscopic septoplasty, minimally invasive approaches, and combined septorhinoplasty procedures for optimal functional and cosmetic results.
Rehabilitation and Support
Postoperative care includes nasal irrigation, follow-up visits, guidance on avoiding trauma, and access to international patient services for smooth recovery.
Advantages of receiving treatment in Korea: skilled ENT surgeons, state-of-the-art technology, minimally invasive techniques, precise correction for breathing improvement, and cost-effective care for international patients.