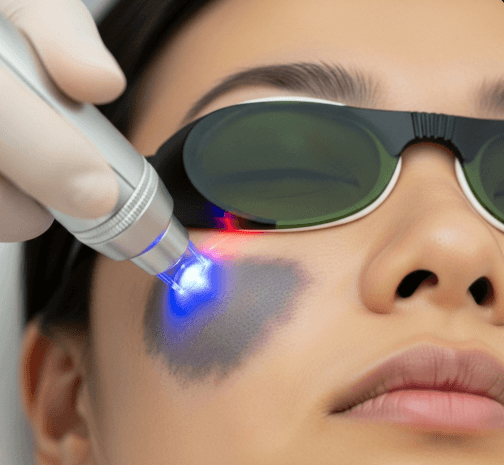
Nevus of Ota Laser Treatment in Korea is a highly specialized dermatological procedure designed to treat bluish-gray or brown pigmentation that appears on the face, typically around the eyes, temple, and sometimes the sclera (white part of the eye). This condition is more common in Asian populations and is caused by an overgrowth of melanocytes in the dermis.
Korea, a global leader in advanced dermatology and pigmentation care, has perfected laser treatments for Nevus of Ota using Q-switched Nd:YAG and Pico lasers. Korean dermatologists are internationally recognized for their ability to deliver safe, gradual, and effective results for this complex condition, especially in patients with Asian skin tones prone to pigmentation rebound.
What It Is
Nevus of Ota is a type of dermal melanocytosis, meaning pigment cells are located deep in the dermis. It appears as bluish, gray, or brown patches around the eye and temple and may extend to the sclera of the eye.
Key characteristics:
- Present at birth or develops during adolescence.
- More common in women and Asian populations.
- Benign in most cases, but cosmetically distressing.
- Can rarely be associated with glaucoma or other eye conditions.
Because pigmentation is deep in the skin, surface-level treatments like creams or chemical peels are ineffective. Laser therapy is the gold standard worldwide, and Korean clinics are leaders in this field.
Why It’s Done
Patients seek Nevus of Ota treatment in Korea for:
- Cosmetic improvement → To achieve clearer, even-toned skin.
- Psychological well-being → Visible pigmentation on the face can affect self-confidence.
- Cultural aesthetics → Clear, spotless skin is central to Korean beauty ideals.
- Preventive monitoring → Rarely, pigment cells may undergo changes, so regular care ensures long-term safety.
Since Nevus of Ota does not fade naturally, treatment is usually a long-term investment in appearance and confidence.
Alternatives
While laser therapy is the most effective option, other supportive measures are available:
- Q-switched Nd:YAG (1064 nm) → Standard for deep pigmentation.
- Pico lasers (PicoWay, PicoSure Pro) → Break pigment into smaller fragments for faster clearance.
- Alexandrite laser (755 nm) → Sometimes used but less effective for deep dermal pigment.
- Camouflage makeup → Temporary concealment, common for patients not yet ready for lasers.
- Observation only → In mild or stable cases, treatment may be delayed.
Preparation
Korean dermatology clinics conduct detailed assessments before beginning laser treatment:
- Consultation → Imaging tools are used to determine pigment depth.
- Medical evaluation → Patients with eye involvement may require an ophthalmology check.
- Pre-care instructions → Avoid sun exposure, tanning, and harsh skincare for 1–2 weeks prior.
- Skin preparation → Hydrating creams and sheet masks to strengthen the barrier.
For laser procedures, numbing cream is usually applied before treatment to ensure comfort.
How It’s Done
A Nevus of Ota laser treatment session in Korea typically lasts 30–45 minutes:
- Cleansing – Removal of makeup and impurities.
- Numbing cream – Applied for 20–30 minutes.
- Laser application –
- Q-switched Nd:YAG (1064 nm) or Pico laser is used.
- Multiple passes deliver energy deep into the dermis to fragment melanin clusters.
- Laser fluence is adjusted carefully to minimize risk of hyperpigmentation.
- Post-care – Cooling masks, soothing creams, and antioxidant serums.
- Final step – Sunscreen applied before discharge.
Most patients require 5–10 sessions spaced 4–8 weeks apart for visible and long-term improvement.
Recovery
Recovery is mild but gradual:
- Immediately after → Redness, swelling, or slight darkening of treated areas.
- 3–7 days later → Pigmented areas may crust or scab lightly before fading.
- 2–4 weeks later → Pigmentation gradually lightens as melanin fragments are cleared.
- Long-term → Ongoing sessions produce progressive fading over months.
Korean clinics enhance recovery with hydration facials, calming ampoules, and LED therapy. Strict SPF 50+ sun protection is mandatory after each session.
Complications
Nevus of Ota laser treatment is safe when performed by experts, but side effects can occur:
- Temporary redness and swelling.
- Mild scabbing or crusting.
- Hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation if aftercare is neglected.
- Rare recurrence of pigmentation over time.
Korean dermatologists minimize risks by using conservative laser settings and multi-session protocols, ensuring safe and natural results.
Treatment Options
Korean clinics offer specialized Nevus of Ota programs:
- Q-switched Nd:YAG laser packages → Standard and widely used.
- Pico laser programs → Advanced, faster pigment clearance with fewer risks.
- Brightening programs → Laser treatment plus Vitamin C or tranexamic acid infusions.
- Combination therapies → Laser treatment with Aqua Peel or Hydrafacial for hydration.
- Maintenance packages → Periodic follow-ups to manage recurrence.
Clinics in Seoul, particularly in Gangnam, provide multi-session deals for both locals and international patients seeking high-quality care at competitive prices.
Conclusion
Nevus of Ota Laser Treatment in Korea is one of the most effective and trusted methods for clearing deep dermal pigmentation around the eye and facial areas. Using Q-switched Nd:YAG and Pico lasers, Korean dermatologists achieve safe, gradual, and long-lasting results while minimizing risks for pigmentation-prone Asian skin.
With world-class technology, tailored protocols, and holistic aftercare, Korea remains a global leader in treating Nevus of Ota. For patients seeking to restore clear, even-toned skin and improve confidence, Korean laser treatments provide a reliable and advanced solution.