Overview
Xerophthalmia is a serious eye condition caused by a severe deficiency of vitamin A. It primarily affects the surface of the eyes, leading to dryness, damage to the cornea, and even blindness if left untreated. It is most common in children and pregnant women in developing regions where malnutrition is prevalent. Early diagnosis and vitamin A supplementation are key to preventing vision loss.
What is
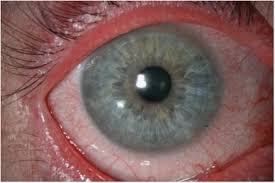
Xerophthalmia is a progressive eye disorder that results from a deficiency in vitamin A. It begins with night blindness and can advance to dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea, leading to ulceration, keratomalacia (corneal softening), and permanent blindness. Xerophthalmia is one of the leading causes of preventable childhood blindness worldwide and is considered a medical emergency when advanced.
Symptoms
- Night blindness (difficulty seeing in low light)
- Dryness of the eyes and conjunctiva
- Bitot’s spots (foamy patches on the white of the eyes)
- Eye redness and irritation
- Blurred vision
- Corneal ulcers or scarring
- Complete vision loss in advanced cases
Causes
Xerophthalmia is primarily caused by vitamin A deficiency, which plays a critical role in maintaining healthy vision, immune function, and epithelial tissues. Other contributing causes include:
- Malnutrition due to poor diet
- Digestive disorders that impair vitamin A absorption (e.g., celiac disease, Crohn’s disease)
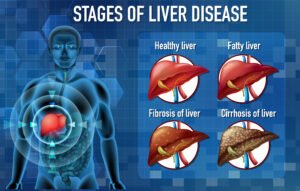
- Liver disease affecting vitamin A storage
- Chronic infections or illnesses that increase vitamin A needs
Risk Factors
- Children under 5 years with poor nutrition
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women in low-income settings
- Malnourished populations or those with limited access to animal-based foods
- People with gastrointestinal disorders that reduce nutrient absorption
- Refugee or displaced populations facing food insecurity
Complications
- Permanent blindness, especially in children
- Corneal perforation and scarring
- Increased risk of eye infections
- Delayed growth and development in children
- Higher mortality rates, particularly in children with measles or diarrhea
- Systemic immune suppression, leading to other infections
Prevention
Preventing xerophthalmia centers around ensuring adequate vitamin A intake and overall nutritional health:
- Balanced diet rich in vitamin A sources (liver, eggs, dairy, dark leafy greens, carrots, mangoes)
- Vitamin A supplementation programs in high-risk populations
- Exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life
- Health education on nutrition and early signs of deficiency
- Public health interventions targeting maternal and child health
- Management of gastrointestinal diseases to improve nutrient absorption
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, medical care for xerophthalmia involves:
- High-dose vitamin A supplementation, usually in capsule form, to rapidly restore levels
- Nutritional support and dietary counseling to correct underlying malnutrition
- Ophthalmic treatment, including artificial tears, antibiotic eye drops, and protective eye care for corneal damage
- Hospitalization, if there are severe corneal ulcers or vision-threatening complications
- Management of underlying conditions such as liver or digestive diseases
Follow-up with nutrition specialists and ophthalmologists ensures both the eye condition and the root cause (vitamin A deficiency) are addressed effectively. Early intervention can restore vision and prevent blindness in most cases.