Overview
Frostbite is a condition where skin and underlying tissues freeze due to prolonged exposure to extreme cold. It can result in permanent tissue damage if not treated promptly. In Korea, frostbite is most commonly seen during harsh winter months, particularly among people who work outdoors, hikers, and mountaineers in mountainous regions. Awareness and preventive measures are important to avoid serious injury or amputation.
What is Frostbite?
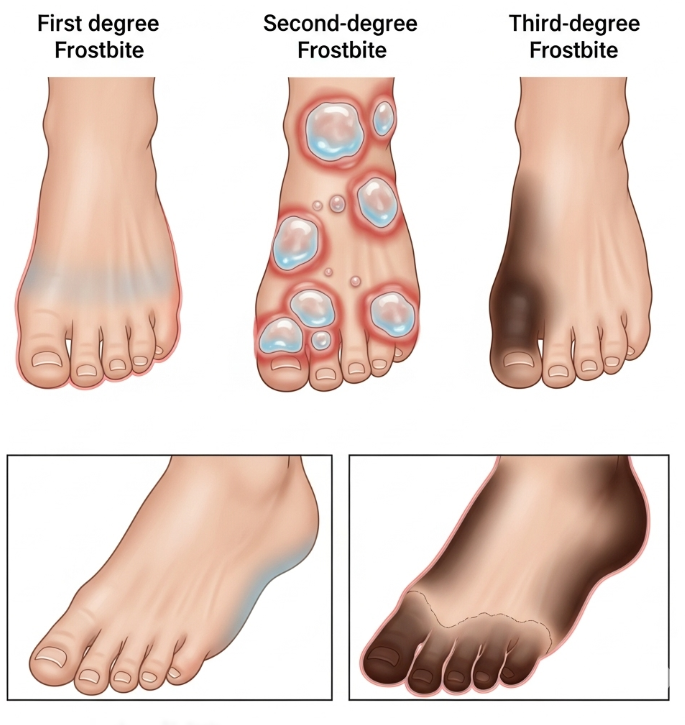
Frostbite occurs when skin and tissues are exposed to freezing temperatures, causing ice crystal formation in cells and restricted blood flow. It commonly affects fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks, and chin. The severity of frostbite ranges from mild (superficial) to severe (deep tissue), potentially leading to permanent tissue damage.
Anyone exposed to cold environments without adequate protection is at risk, particularly children, elderly, and people with circulation issues.
Symptoms
- Cold, numb, or tingling skin in affected areas
- Pale, white, or bluish skin
- Hard or waxy texture of the skin
- Blisters in more severe cases
- Swelling and redness during rewarming
- Severe cases may cause blackened tissue (necrosis)
Causes
- Prolonged exposure to freezing temperatures
- Wet or damp clothing in cold weather
- Wind chill, which accelerates heat loss
- Direct contact with frozen metal or surfaces
- Reduced circulation due to underlying medical conditions
Risk Factors
- Working or playing outdoors in winter
- Inadequate clothing or protective gear
- Peripheral vascular disease or diabetes
- Smoking, which reduces blood flow
- Alcohol consumption, which impairs body temperature regulation
- Age extremes: infants and elderly
Complications
- Permanent tissue damage or gangrene
- Amputation in severe cases
- Infections in damaged skin
- Nerve damage leading to chronic numbness or pain
- Hypothermia if frostbite occurs alongside prolonged cold exposure
Prevention
- Wear insulated clothing, gloves, socks, and footwear
- Keep skin dry and avoid prolonged exposure to cold
- Layer clothing to retain body heat
- Avoid alcohol and smoking in cold conditions
- Monitor for early signs such as tingling or pale skin
- Seek shelter during extreme cold weather warnings
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Physical examination to assess the extent of tissue damage
- Imaging (X-ray, MRI) for deep tissue involvement
- Monitoring circulation in affected areas
Medical Treatments
- Rapid but careful rewarming in warm water baths (37–39°C)
- Pain management with analgesics or NSAIDs
- Topical or systemic antibiotics if infection occurs
- Thrombolytic therapy in severe frostbite to improve blood flow
Surgical & Advanced Therapies
- Debridement of dead tissue
- Skin grafting or reconstructive surgery for severe tissue loss
- Amputation in cases of irreversible necrosis
Supportive Care & Rehabilitation
- Physical therapy to restore mobility in affected areas
- Protective dressings and wound care
- Long-term monitoring for nerve damage or chronic pain