Overview
Fibrillation refers to irregular, rapid, and uncoordinated contractions of the heart’s muscle fibers, leading to abnormal heart rhythms. The most common type is atrial fibrillation (AFib), but ventricular fibrillation (VFib) can also occur and is considered a medical emergency. In Korea, fibrillation is a growing health concern due to an aging population, lifestyle factors, and rising cardiovascular diseases. Korean hospitals use advanced cardiac monitoring, minimally invasive procedures, and catheter ablation therapies to manage fibrillation effectively.
What is Fibrillation?
Fibrillation is a type of cardiac arrhythmia where the heart’s electrical impulses become chaotic, causing the chambers to quiver instead of contracting properly.
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib): Common and often chronic, leading to an increased risk of stroke.
- Ventricular fibrillation (VFib): Life-threatening, requiring immediate CPR and defibrillation.
Symptoms
- Irregular or rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or fainting
- Chest pain (especially in VFib)
- Anxiety due to awareness of heartbeat
Causes
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart valve disorders
- Thyroid disease
- Excessive alcohol intake (“holiday heart syndrome”)
- Genetic predisposition
- Previous heart surgery
- Chronic lung disease
Risk Factors
- Age over 60
- Family history of heart disease
- Diabetes
- Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
- Sleep apnea
- Smoking and alcohol use
Complications
- Stroke (blood clots from atrial fibrillation)
- Heart failure
- Sudden cardiac arrest (from ventricular fibrillation)
- Reduced quality of life due to fatigue and irregular rhythm
Prevention
- Control blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes
- Maintain a healthy weight and diet
- Avoid excessive alcohol and caffeine
- Regular physical activity
- Quit smoking
- Regular check-ups with a cardiologist
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
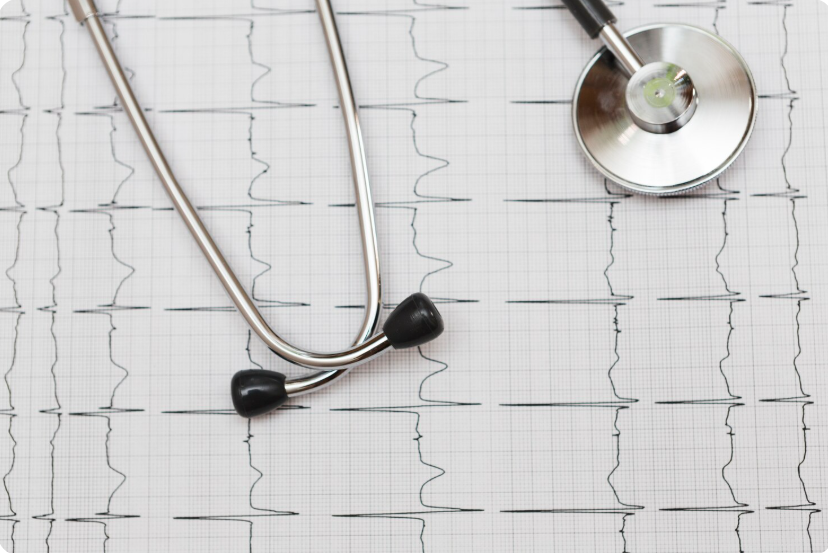
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG)
- Holter monitoring (24–48 hours)
- Echocardiogram for structural evaluation
- Cardiac MRI/CT for advanced imaging
- Blood tests (thyroid, electrolytes)
Medical Treatments
- Antiarrhythmic medications (amiodarone, flecainide)
- Rate control drugs (beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers)
- Anticoagulants (warfarin, NOACs) to prevent stroke
- Lifestyle modification programs in Korea’s cardiac rehabilitation centers
Surgical & Advanced Therapies
- Catheter ablation – advanced treatment widely available in Korean hospitals
- Electrical cardioversion – restoring normal rhythm with controlled shocks
- Pacemaker or ICD (implantable cardioverter-defibrillator) for severe cases
- Left atrial appendage closure devices to reduce stroke risk in AFib patients
Rehabilitation and Support in Korea
- Specialized cardiac rehabilitation programs with exercise training and lifestyle coaching
- Patient education for medication adherence and stroke prevention
- Long-term follow-ups with cardiologists for monitoring recurrence