Overview
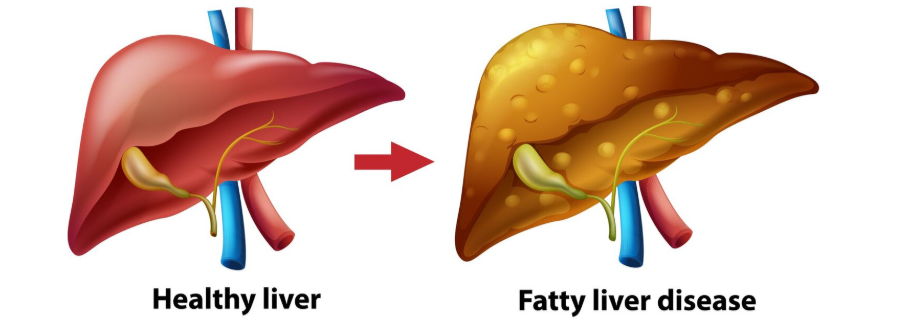
Fatty liver disease (FLD) is a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, which can be either alcohol-related (AFLD) or non-alcoholic (NAFLD). In Korea, FLD is increasingly prevalent due to dietary habits, sedentary lifestyles, and rising rates of obesity and diabetes. Timely diagnosis and management are crucial to prevent progression to liver inflammation, fibrosis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease occurs when fat builds up in the liver beyond normal levels. NAFLD is the most common type in Korea, often linked to metabolic syndrome, diabetes, and obesity, while AFLD is caused by excessive alcohol consumption. Many patients are asymptomatic initially, making screening and routine liver tests important.
Symptoms
- Often asymptomatic in early stages
- Fatigue or general malaise
- Discomfort or pain in the upper right abdomen
- Unexplained weight loss in advanced cases
- Swelling in the abdomen or legs (edema in severe cases)
- Elevated liver enzymes on routine blood tests
Causes
- Excessive alcohol consumption (for AFLD)
- Obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes (for NAFLD)
- High-fat and high-sugar diet
- Certain medications (e.g., corticosteroids, tamoxifen)
- Genetic predisposition
Risk Factors
- Obesity and overweight
- Type 2 diabetes or prediabetes
- High cholesterol or triglycerides
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Age over 40
- Family history of liver disease
Complications
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
- Liver fibrosis and cirrhosis
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer)
- Increased cardiovascular disease risk
- Liver failure in advanced stages
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight and balanced diet
- Engage in regular physical activity
- Limit or avoid alcohol consumption
- Control blood sugar, cholesterol, and triglyceride levels
- Regular liver function tests for high-risk individuals
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Blood tests for liver enzymes (ALT, AST)
- Ultrasound, CT, or MRI to detect fat accumulation
- FibroScan to assess liver fibrosis
- Liver biopsy for definitive diagnosis in complex cases
Medical Treatments
- Lifestyle modification: diet, exercise, and weight loss
- Medications for diabetes, high cholesterol, or triglycerides
- Hepatoprotective agents in selected patients
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Bariatric surgery for obese patients with NAFLD/NASH
- Liver transplantation in end-stage liver disease
- Clinical trials for emerging therapies in specialized centers
Rehabilitation and Support
- Nutritional counseling and structured exercise programs
- Regular monitoring of liver function and metabolic health
- Support groups for lifestyle management and chronic disease