Overview
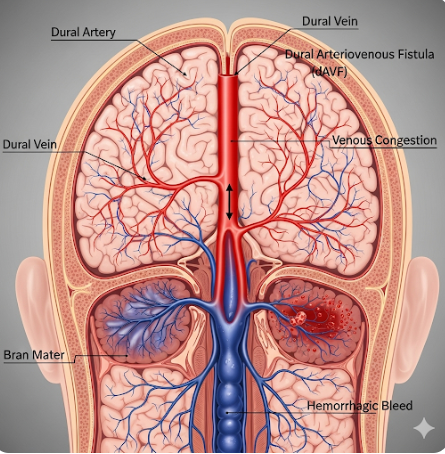
A dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) is an abnormal connection between an artery and a vein in the dura mater of the brain or spinal cord. In South Korea, this condition is rare but clinically significant, as it can lead to neurological symptoms and, in severe cases, hemorrhage. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and preserve neurological function.
What is Dural Arteriovenous Fistula?
Dural arteriovenous fistulas are abnormal shunts that bypass the capillary system, allowing direct flow of arterial blood into veins. They can occur intracranially or in the spinal dura and may present at any age. Symptoms depend on the location and size of the fistula and the pattern of venous drainage.
Symptoms
Symptoms of DAVF may include:
- Headache or pulsatile tinnitus (in cranial DAVF)
- Neurological deficits such as weakness, numbness, or vision changes
- Seizures
- Intracranial or spinal hemorrhage in severe cases
- Cognitive or behavioral changes if venous congestion affects brain regions
Causes
The exact cause of DAVF is often unclear, but contributing factors include:
- Trauma or injury to the brain or spinal cord
- Previous surgery or sinus thrombosis
- Age-related vascular changes
- Congenital vascular malformations in some cases
Risk Factors
Risk factors for developing DAVF include:
- History of head or spinal trauma
- Previous cranial or spinal surgery
- Age over 50 (for acquired cranial DAVF)
- Thrombosis or occlusion of dural sinuses
Complications
Potential complications of untreated DAVF include:
- Intracranial or spinal hemorrhage
- Permanent neurological deficits
- Seizures and chronic headaches
- Venous hypertension leading to cognitive or motor impairments
Prevention
Preventive measures focus on managing underlying risk factors:
- Avoiding head or spinal trauma
- Prompt treatment of sinus thrombosis
- Regular monitoring for individuals with previous cranial or spinal surgery
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment in South Korea is specialized and often involves a multidisciplinary approach:
Endovascular Therapy:
- Catheter-based embolization to close the abnormal connection
- Minimally invasive and often first-line treatment
Surgical Intervention:
- Microsurgical disconnection of the fistula for complex or inaccessible cases
- Craniotomy or laminectomy depending on the location
Supportive Care:
- Symptom management for headaches, seizures, or neurological deficits
- Rehabilitation for neurological recovery post-treatment
Specialized Care:
- Neurosurgery and interventional neuroradiology departments in Korean hospitals provide advanced diagnostic imaging (DSA, MRI, CT angiography)
- Multidisciplinary teams including neurosurgeons, neurologists, and rehabilitation specialists optimize outcomes
With timely diagnosis and modern treatment approaches in Korea, patients with dural arteriovenous fistulas can achieve symptom relief, prevent hemorrhage, and maintain neurological function.