Overview
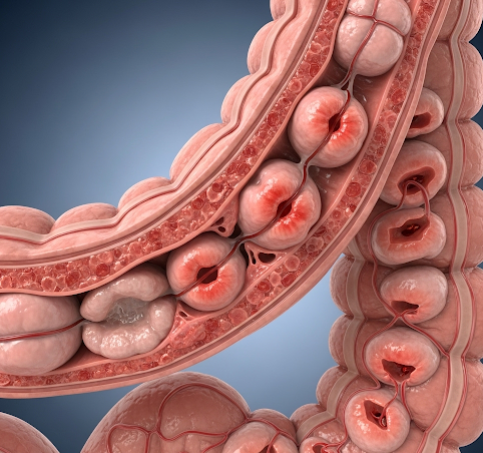
Diverticulitis is an inflammatory condition of the colon caused by the infection or inflammation of diverticula (small pouches in the colon wall). In Korea, gastroenterologists provide diagnosis, medical treatment, and surgical management to reduce complications and improve patient outcomes.
What is Diverticulitis?
Diverticulitis occurs when diverticula become inflamed or infected, leading to symptoms such as abdominal pain, fever, and digestive disturbances. This condition can range from mild cases manageable with medication to severe complications requiring surgery. It primarily affects middle-aged and older adults.
Symptoms
- Lower abdominal pain, usually on the left side
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Abdominal tenderness
- Rectal bleeding in some cases
Causes
- Formation of diverticula due to weak colon walls
- Increased pressure in the colon from constipation
- Low-fiber diet
- Bacterial infection of the diverticula
- Genetic and age-related factors
Risk Factors
- Age over 40
- Low dietary fiber intake
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking
- Use of NSAIDs or corticosteroids
Complications
- Abscess formation in the abdominal cavity
- Fistula formation with bladder or other organs
- Intestinal obstruction
- Perforation of the colon
- Severe bleeding or sepsis in extreme cases
Prevention
- High-fiber diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Regular physical activity
- Adequate hydration
- Avoid smoking and manage body weight
- Prompt medical attention for gastrointestinal symptoms
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- CT scan to assess inflammation and complications
- Colonoscopy after acute symptoms resolve to evaluate the colon
- Blood tests to check for infection and inflammation
- Stool tests to rule out other conditions
Medical Treatments
- Antibiotics to treat bacterial infection
- Pain management with analgesics
- Liquid or soft diet during flare-ups to reduce colon stress
- Probiotics to maintain gut health
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Resection of affected colon segment for recurrent or severe cases
- Laparoscopic surgery for minimally invasive treatment
- Abscess drainage if localized collections form
Rehabilitation and Support
- Gradual return to a regular diet after inflammation
- Nutrition counseling for fiber-rich diet
- Lifestyle modifications to prevent recurrence
- Follow-up colonoscopy to monitor colon health