Overview
Diverticular disease is a common digestive condition characterized by the formation of small pouches (diverticula) in the colon wall. In Korea, gastroenterologists provide diagnosis, dietary guidance, and medical or surgical treatment to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
What is Diverticular Disease?
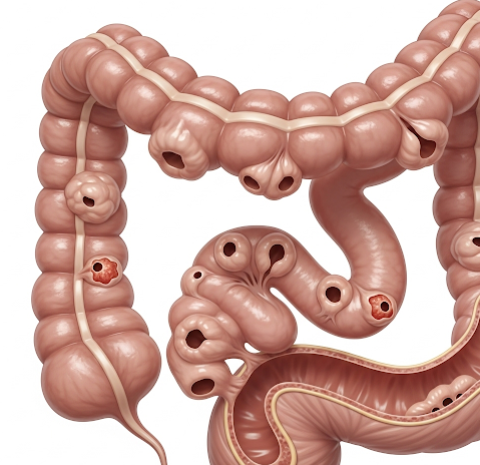
Diverticular disease occurs when diverticula (small sac-like protrusions) develop in the colon, particularly the sigmoid colon. It includes diverticulosis (presence of diverticula without inflammation) and diverticulitis (inflammation or infection of diverticula). The condition primarily affects older adults, though prevalence is rising in younger populations due to dietary and lifestyle changes.
Symptoms
- Abdominal pain, usually in the lower left quadrant
- Bloating and gas
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Nausea and mild fever in inflammation
- Rectal bleeding or blood in stool in severe cases
- Tenderness in the abdomen
Causes
- Weak spots in the colon wall
- Increased pressure inside the colon due to constipation
- Age-related degeneration of connective tissue
- Low-fiber diet contributing to harder stools
- Genetic predisposition
Risk Factors
- Age over 40
- Low-fiber diet
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Certain medications like NSAIDs
Complications
- Diverticulitis (infection and inflammation)
- Abscess formation in the abdomen
- Fistula between colon and bladder or other organs
- Intestinal obstruction
- Severe bleeding or perforation
Prevention
- High-fiber diet (fruits, vegetables, whole grains)
- Regular physical activity
- Adequate hydration
- Avoid smoking and manage weight
- Early medical evaluation for gastrointestinal symptoms
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Colonoscopy to visualize diverticula
- CT scan to assess diverticulitis or complications
- Blood tests to check for infection and inflammation
- Stool tests to rule out other causes
Medical Treatments
- Antibiotics for diverticulitis
- Pain management with analgesics
- Diet modification with high-fiber intake
- Probiotics to support gut health
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Resection of affected colon segment in severe or recurrent cases
- Laparoscopic surgery for minimally invasive treatment
- Drainage of abscesses if present
Rehabilitation and Support
- Gradual reintroduction of solid foods after inflammation
- Nutrition counseling for a high-fiber diet
- Monitoring for recurrence through follow-up colonoscopy
- Education on lifestyle modifications to prevent flare-ups