Overview
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. In Korea, it affects a smaller proportion of the population compared to Type 2, but early diagnosis and insulin therapy are crucial to prevent complications. Specialized pediatric and adult endocrinology centers provide comprehensive management.
What is Diabetes (Type 1)?
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks pancreatic beta cells, leading to insulin deficiency. It can develop at any age, but often appears in children and adolescents. Lifelong insulin therapy and careful monitoring of blood glucose are essential for management.
Symptoms
- Frequent urination and excessive thirst
- Increased hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Nausea or vomiting in severe cases (diabetic ketoacidosis)
Causes
- Autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells
- Genetic susceptibility
- Possible environmental triggers such as viral infections
- No direct link to lifestyle factors
Risk Factors
- Family history of Type 1 diabetes
- Genetic predisposition (HLA gene variants)
- Presence of other autoimmune conditions (thyroid disease, celiac disease)
- Childhood or adolescence (typical onset age)
Complications
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) if untreated
- Cardiovascular disease
- Kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy)
- Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy)
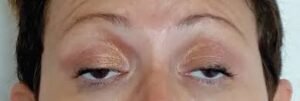
- Eye complications (retinopathy, glaucoma)
- Increased risk of infections
Prevention
- No proven prevention for autoimmune onset
- Early recognition and prompt insulin therapy reduce acute and long-term complications
- Regular monitoring for high-risk individuals with family history
Treatment Options in Korea
- Diagnosis
- Fasting blood glucose and HbA1c tests
- C-peptide test to assess insulin production
- Autoantibody testing (GAD, IA-2 antibodies)
- Medical Treatments
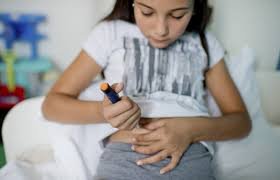
- Insulin therapy (injections or insulin pumps)
- Continuous glucose monitoring systems for precise blood sugar tracking
- Lifestyle management: balanced diet and physical activity
- Management of associated autoimmune conditions
- Rehabilitation & Support
- Diabetes education for patients and families
- Nutritional counseling for carbohydrate management
- Psychological support for chronic disease coping
- Regular follow-up for early detection of complications