Overview
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion. In Korea, its prevalence has increased due to urbanization, dietary changes, and sedentary lifestyles, making early detection and management critical to prevent complications.
What is Diabetes (Type 2)?
Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body cannot effectively use insulin, often combined with reduced insulin production. It typically develops in adults over 40, but younger populations are increasingly affected due to obesity and lifestyle factors.
Symptoms
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Fatigue or weakness
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Recurrent infections
Causes
- Insulin resistance caused by obesity and inactivity
- Gradual decline in insulin production by pancreatic beta cells
- Genetic predisposition and family history
- Poor diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugar
Risk Factors
- Overweight or obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of Type 2 diabetes
- Age over 40 years (but can affect younger adults)
- High blood pressure or cholesterol
- History of gestational diabetes
Complications
- Cardiovascular disease (heart attack, stroke)
- Kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy)
- Nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy)
- Eye complications (retinopathy, cataracts, glaucoma)
- Foot ulcers and infections
- Increased susceptibility to infections
Prevention
- Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise
- Regular physical activity
- Balanced diet with high fiber and low sugar
- Routine blood sugar screening, especially for high-risk individuals
- Management of blood pressure and cholesterol
Treatment Options in Korea
- Diagnosis
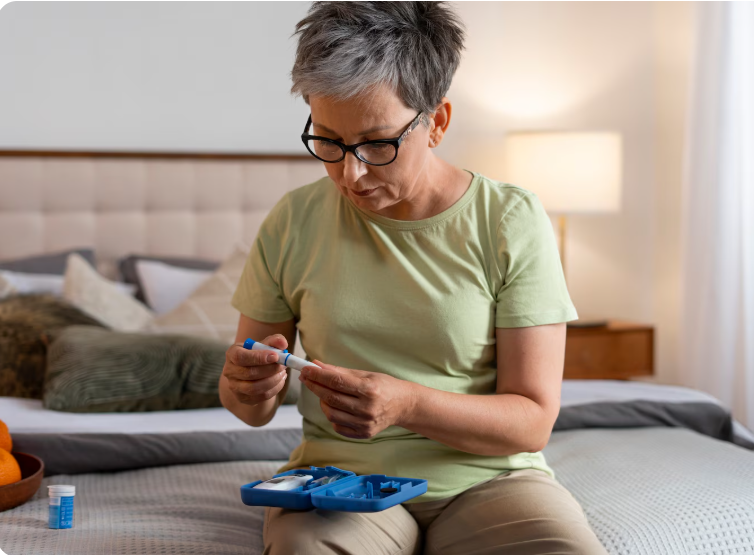
- Fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, oral glucose tolerance tests
- Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels
- Medical Treatments
- Lifestyle modifications: diet, exercise, weight control
- Oral hypoglycemic agents (metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors)
- Insulin therapy in advanced cases
- Management of comorbidities like hypertension and dyslipidemia
- Rehabilitation & Support
- Diabetes education programs for self-management
- Nutrition counseling
- Blood sugar self-monitoring guidance
- Support groups for lifestyle adherence and motivation