Overview
Dental caries, commonly known as tooth decay, is a widespread dental condition caused by the breakdown of tooth enamel due to bacterial activity. In Korea, routine dental check-ups and preventive care are emphasized, with hospitals such as Seoul National University Dental Hospital, Asan Medical Center Dental Clinic, and Samsung Medical Center Dental Department providing comprehensive treatment.
What is Dental Caries?
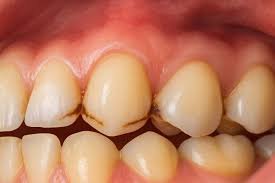
Dental caries is the destruction of tooth structure by acid-producing bacteria. It usually begins with enamel demineralization and can progress to affect dentin and pulp if untreated. Both children and adults are susceptible, and poor oral hygiene, diet high in sugar, and lack of preventive care are major contributors.
Symptoms
- Toothache or spontaneous pain
- Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks
- Visible pits, holes, or dark spots on teeth
- Bad breath or unpleasant taste
- Swelling or tenderness around affected teeth
- Difficulty chewing or biting
Causes
- Acid produced by bacteria (Streptococcus mutans) metabolizing sugars
- Poor oral hygiene leading to plaque accumulation
- Frequent consumption of sugary or acidic foods
- Dry mouth conditions reducing saliva protection
- Tooth misalignment making cleaning difficult
Risk Factors
- Inadequate brushing and flossing
- High-sugar diet and frequent snacking
- Lack of fluoride exposure
- Genetic susceptibility
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Chronic medical conditions such as diabetes
Complications
- Progression to dental abscess or infection
- Tooth loss if decay is untreated
- Pain affecting eating and nutrition
- Spread of infection to jaw or systemic illness in severe cases
- Aesthetic issues and speech problems
Prevention
- Brush teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth
- Regular dental check-ups and cleanings
- Reduce intake of sugary and acidic foods
- Use dental sealants for children at high risk
- Maintain proper hydration to stimulate saliva production
Treatment Options in Korea
Treatment depends on the stage of decay and severity.
- Diagnosis
- Visual examination and probing
- Dental X-rays to detect cavities between teeth
- Assessment of oral hygiene and dietary habits
- Review of medical and dental history
- Medical Treatments
- Fluoride treatments for early enamel demineralization
- Fillings for cavities (composite or amalgam)
- Root canal therapy for pulp involvement
- Extraction of irreparably damaged teeth
- Antibiotics if secondary infection occurs
- Supportive Care
- Pain management with analgesics
- Oral hygiene education and dietary counseling
- Monitoring for new cavities during follow-up visits
- Use of protective dental sealants in children
- Specialized Hospitals and Clinics in Korea
- Seoul National University Dental Hospital – Preventive dentistry and restorative care
- Asan Medical Center Dental Clinic – Comprehensive dental services
- Samsung Medical Center Dental Department – Advanced restorative and endodontic care
- Local dental clinics for routine preventive care
- Long-Term Follow-Up
- Regular dental exams and cleaning
- Fluoride treatments and sealants as needed
- Education on proper brushing and dietary habits
- Monitoring for recurrence and management of underlying risk factors