Overview
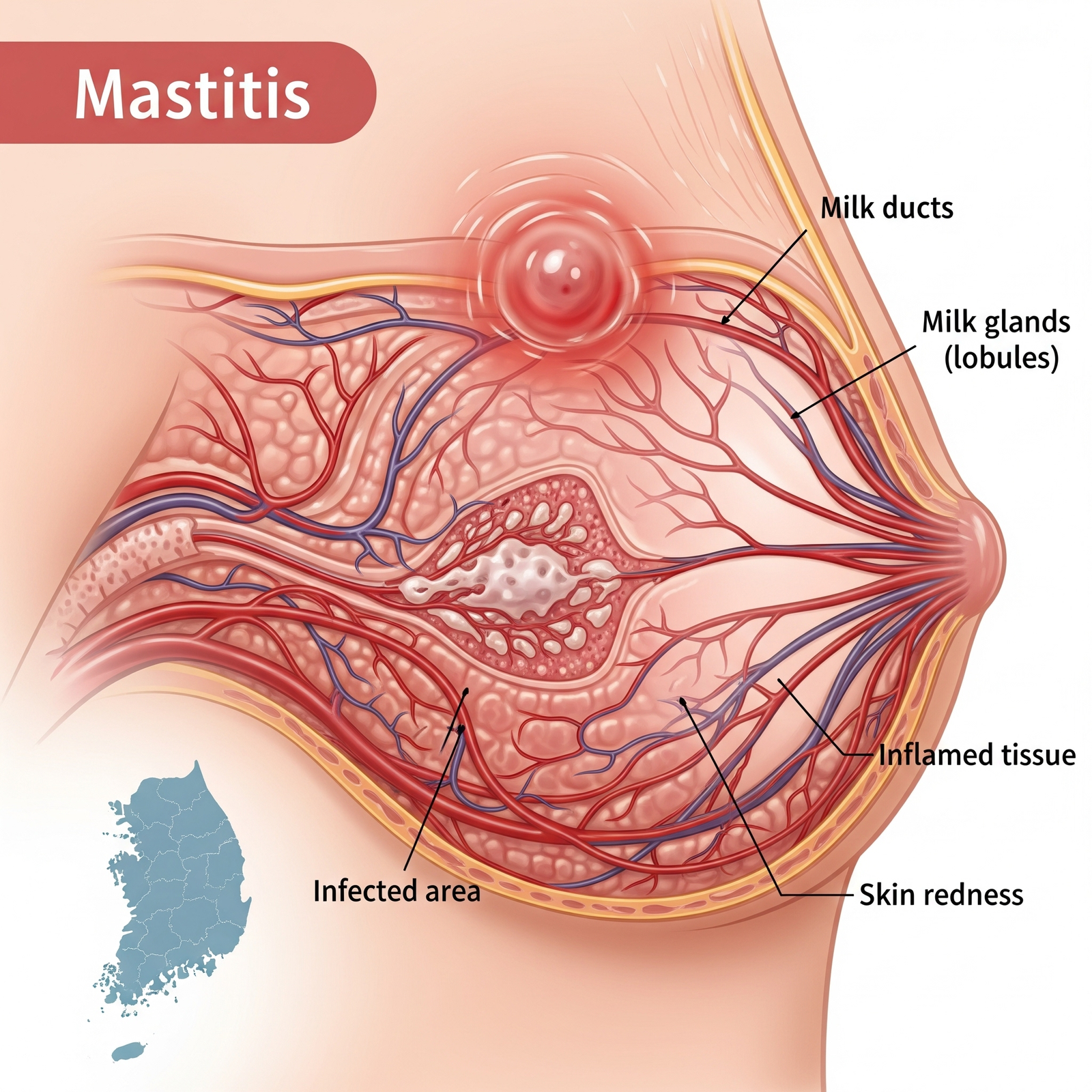
Mastitis is an inflammatory condition of the breast, often caused by infection, leading to pain, swelling, and redness. In Korea, mastitis is commonly seen in breastfeeding women, but non-lactational cases also occur. Korean hospitals provide rapid diagnosis, antibiotic therapy, and supportive care to prevent complications.
What is Mastitis?
Mastitis is the inflammation of breast tissue, typically due to bacterial infection, blocked milk ducts, or underlying conditions. It primarily affects women during lactation but can also occur in non-lactating women and men. The condition can cause systemic symptoms like fever and malaise if untreated.
Symptoms
- Breast pain and tenderness
- Swelling and redness of the affected breast
- Warmth over the inflamed area
- Fever and chills
- Nipple discharge (occasionally pus)
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Lump or thickening in the breast
Causes
- Bacterial infection, commonly Staphylococcus aureus
- Blocked milk ducts during breastfeeding
- Cracked or damaged nipples allowing bacterial entry
- Trauma or injury to the breast
- Underlying chronic conditions such as diabetes
Risk Factors
- Lactation, especially in first-time mothers
- Poor breastfeeding technique or incomplete emptying of breast
- History of mastitis or breast infections
- Smoking, which may impair immune response
- Chronic illnesses like diabetes or immune deficiency
Complications
- Formation of breast abscess
- Recurrent infections
- Reduced milk supply in breastfeeding women
- Systemic infection if untreated (rare)
- Pain or scarring in severe cases
Prevention
- Proper breastfeeding techniques to ensure complete milk removal
- Good hygiene and handwashing before breastfeeding
- Regular breast care and monitoring for early signs of infection
- Avoiding tight or restrictive clothing
- Seeking prompt medical care for nipple cracks or signs of infection
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Clinical examination to assess swelling, redness, and tenderness
- Ultrasound imaging to detect abscesses
- Milk or nipple swabs to identify causative bacteria
- Blood tests if systemic infection is suspected
Medical & Surgical Treatments
- Antibiotic therapy targeted to the causative bacteria
- Pain relief medications such as acetaminophen or NSAIDs
- Incision and drainage for abscess formation
- Warm compresses and supportive care
- Continuation of breastfeeding or expressed milk to maintain milk flow
Rehabilitation and Support
- Breastfeeding counseling for proper techniques
- Education on early recognition of infection
- Nutritional support to promote healing
- Follow-up to monitor recurrence or complications
- Psychological support for stress or anxiety related to breastfeeding challenges