Overview
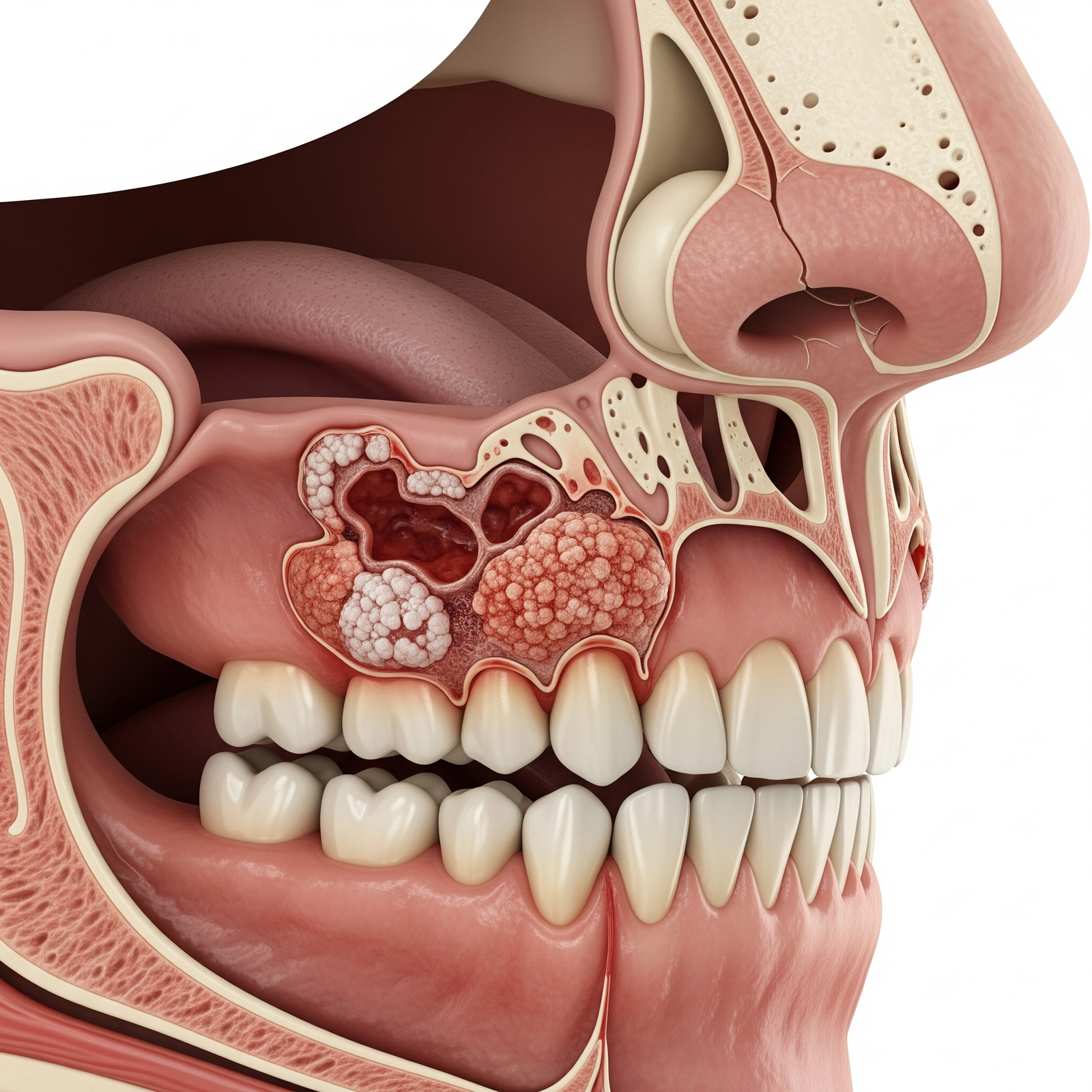
Hard palate cancer is a rare form of oral cancer that originates in the hard palate—the bony front portion of the roof of the mouth. It can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty eating or speaking.
In Korea, hard palate cancer is diagnosed and treated in specialized oncology and maxillofacial surgery centers, with a focus on early detection, surgical intervention, radiation, and reconstructive techniques to improve outcomes.
What is Hard Palate Cancer?
Hard palate cancer is a malignant tumor that develops from the epithelial cells lining the hard palate. The most common type is squamous cell carcinoma, which can invade local tissues and spread to nearby lymph nodes. It primarily affects adults over 50 years old, with risk factors including tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and chronic irritation.
Symptoms
- Persistent pain or discomfort in the roof of the mouth
- Visible lump, ulcer, or white/red patch on the hard palate
- Bleeding from the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Loose teeth or changes in dental alignment
- Swelling or numbness in the palate or surrounding areas
Causes
- Chronic irritation from ill-fitting dentures or rough teeth
- Tobacco use (smoking or chewing)
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Genetic susceptibility and age-related factors
Risk Factors
- Age over 50 years
- Tobacco and alcohol use
- Poor oral hygiene
- HPV infection
- Family history of oral or head and neck cancers
- Long-term irritation from dental appliances
Complications
- Spread to nearby tissues, including the nasal cavity and sinuses
- Involvement of lymph nodes in the neck
- Difficulty eating, speaking, or maintaining oral hygiene
- Facial disfigurement if untreated
- Recurrence after treatment
Prevention
- Avoid tobacco and limit alcohol consumption
- Maintain good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups
- Avoid chronic irritation from dental appliances
- HPV vaccination where appropriate
- Early evaluation of any persistent oral lesions
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Physical examination and oral inspection
- Biopsy of suspicious lesions
- Imaging studies: CT, MRI, or PET scans for staging
- Dental evaluation and assessment of adjacent structures
Medical Treatments
- Radiation therapy for localized tumors
- Chemotherapy in combination with radiation for advanced stages
- Targeted therapy for specific molecular markers
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Surgical excision of the tumor with clear margins
- Neck dissection if lymph nodes are involved
- Reconstructive surgery using grafts or flaps to restore function and appearance
- Minimally invasive and robotic-assisted surgical options available in major Korean hospitals
Rehabilitation and Support
- Speech and swallowing therapy post-surgery
- Nutritional support for patients with difficulty eating
- Psychological counseling for coping with cancer and appearance changes
- Regular follow-up for recurrence monitoring