Overview
A heart murmur is an abnormal sound heard during a heartbeat, often described as a whooshing or swishing noise. While many murmurs are harmless (innocent), some indicate underlying heart conditions, such as valve abnormalities or congenital heart defects.
In Korea, heart murmurs are assessed in cardiology clinics, where advanced diagnostics and treatments are available for both pediatric and adult patients.
What is a Heart Murmur?
A heart murmur occurs when blood flow within the heart becomes turbulent, producing an audible sound. Murmurs can be innocent (benign) or pathological, the latter suggesting structural heart problems like valve stenosis, regurgitation, or septal defects.
Symptoms
- Often no symptoms for innocent murmurs
- Shortness of breath (if associated with valve disease)
- Fatigue or weakness
- Chest pain or palpitations
- Swelling in legs or abdomen (advanced cases)
- Cyanosis (bluish skin in congenital defects)
Causes
- Turbulent blood flow through heart valves or septal defects
- Congenital heart defects (present from birth)
- Heart valve diseases (stenosis or regurgitation)
- Anemia or hyperthyroidism (can cause functional murmurs)
- Age-related degenerative changes in adults
Risk Factors
- Congenital heart disease in children
- Aging and valve degeneration in adults
- Family history of heart conditions
- Chronic illnesses affecting blood flow
- Previous heart infections (endocarditis)
Complications
- Heart failure if valve disease progresses
- Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias)
- Stroke risk in certain valve conditions
- Reduced physical capacity and fatigue
- Rarely, severe congenital defects may require urgent intervention
Prevention
- Regular heart check-ups, especially in children and older adults
- Early evaluation of unusual heart sounds
- Management of risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol
- Vaccination against infections that may affect the heart (e.g., rheumatic fever)
- Healthy lifestyle to support cardiovascular health
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Auscultation by a cardiologist to identify murmur type
- Echocardiography to visualize heart valves and chambers
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) for rhythm assessment
- Chest X-ray or cardiac MRI in selected cases
Medical Treatments
- Observation for innocent or asymptomatic murmurs
- Medications to manage associated conditions (e.g., heart failure, high blood pressure)
- Antibiotic prophylaxis for patients at risk of endocarditis
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Valve repair or replacement for significant valve disease
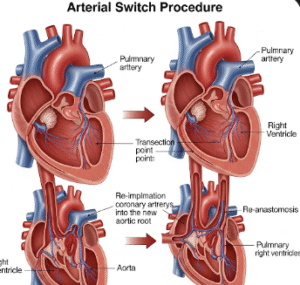
- Septal defect closure for congenital heart anomalies
- Minimally invasive and robotic-assisted cardiac surgery available in Korean hospitals
- Regular follow-up to monitor heart function post-surgery
Rehabilitation and Support
- Cardiac rehabilitation programs for post-surgical patients
- Lifestyle counseling for heart-healthy habits
- Monitoring and adjustment of medications
- Education for parents of children with congenital murmurs