Overview
Hearing loss is a common sensory disorder that can affect people of all ages, from infants to older adults. In Korea, it is a growing health concern due to aging populations, noise exposure, and ear infections, with advanced treatments available in specialized ENT and audiology clinics.
What is Hearing Loss?
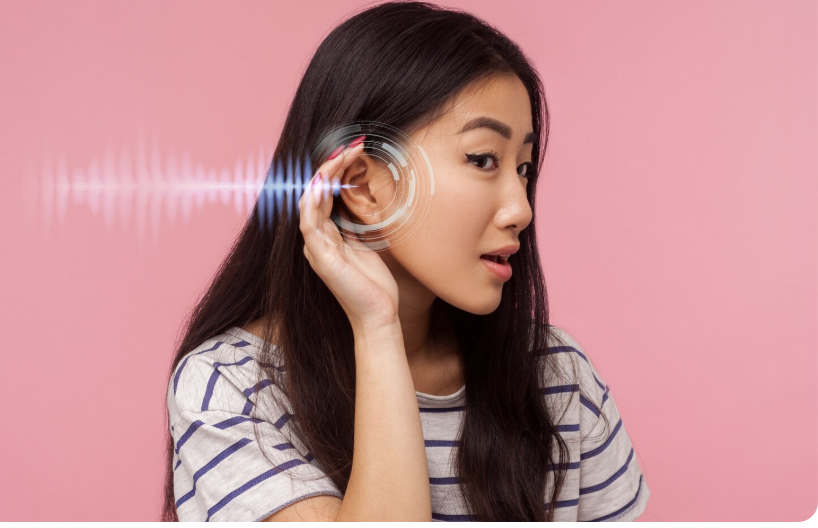
Hearing loss refers to a partial or complete inability to hear sounds. It can be conductive, sensorineural, or mixed, depending on whether the problem lies in the outer/middle ear, inner ear, or both. Hearing loss may affect speech development in children and quality of life in adults.
Symptoms
- Difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy environments
- Asking others to repeat themselves frequently
- Turning up the volume of electronic devices
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Withdrawal from social situations
- In infants: delayed speech or lack of response to sounds
Causes
- Age-related degeneration (presbycusis)
- Chronic ear infections or otitis media
- Exposure to loud noise
- Genetic or congenital conditions
- Trauma to the head or ear
- Ototoxic medications (certain antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs)
Risk Factors
- Older age
- Family history of hearing loss
- Prolonged exposure to loud sounds (industrial, musical, environmental)
- Frequent ear infections or untreated ear conditions
- Certain medical conditions such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease
Complications
- Speech and language delays in children
- Social isolation or communication difficulties
- Cognitive decline associated with hearing impairment
- Emotional issues, including depression or frustration
- Safety risks due to inability to hear alarms or warnings
Prevention
- Use ear protection in noisy environments
- Limit exposure to loud music and sounds
- Prompt treatment of ear infections
- Regular hearing check-ups, especially for children and older adults
- Avoid ototoxic medications when possible or monitor hearing during use
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Audiometry tests to measure hearing thresholds
- Tympanometry to assess middle ear function
- Otoacoustic emissions (OAE) for newborn hearing screening
- Imaging (CT or MRI) if structural issues are suspected
Medical Treatments
- Antibiotics or anti-inflammatory medications for infections
- Earwax removal and treatment of chronic otitis
- Management of underlying medical conditions contributing to hearing loss
Surgical or Advanced Therapies
- Hearing aids for mild to moderate sensorineural loss
- Cochlear implants for severe or profound hearing loss
- Middle ear surgery (tympanoplasty, stapedectomy) for conductive hearing loss
- Bone-anchored hearing systems for specific cases
Rehabilitation and Support
- Speech therapy and auditory training for children
- Counseling on communication strategies for adults
- Follow-up audiometry and hearing aid adjustments
- Support groups for patients with hearing impairment