Overview
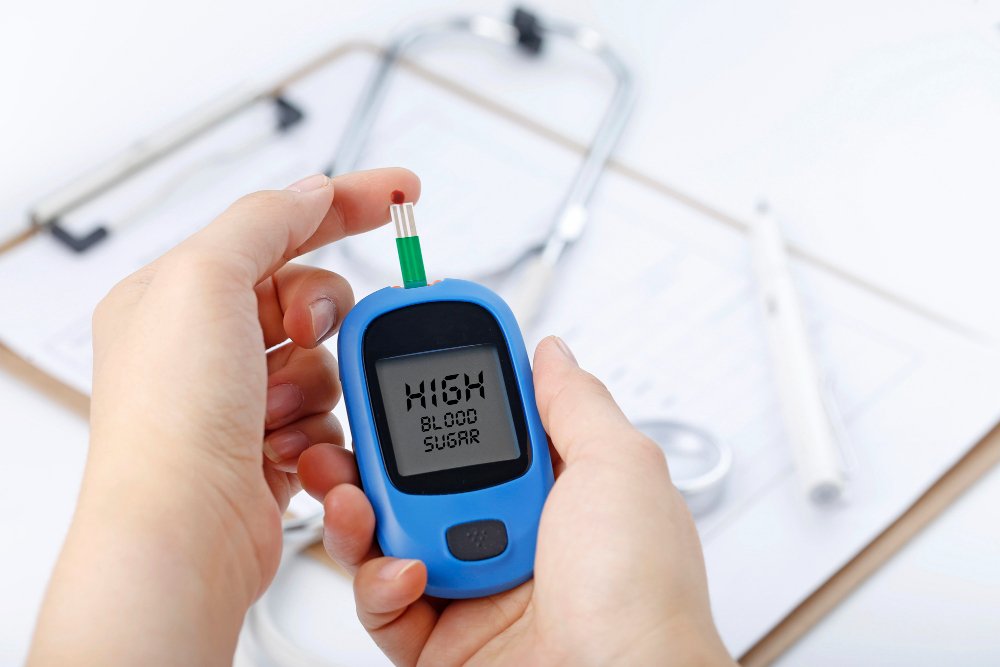
Hyperglycaemia refers to abnormally high levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood, most commonly associated with diabetes mellitus. It can also occur due to stress, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions. Persistent hyperglycaemia may cause damage to blood vessels, nerves, and organs, leading to complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and vision loss.
In Korea, where the prevalence of diabetes has been steadily increasing, hyperglycaemia is a major public health concern. Korean hospitals and clinics provide comprehensive diagnostic services, modern glucose monitoring systems, and advanced treatment options including medication, insulin therapy, lifestyle modification, and digital health support tools.
What is Hyperglycaemia?
Hyperglycaemia occurs when insulin is insufficient or ineffective in regulating glucose uptake by the body’s cells, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. It is typically defined as a fasting blood glucose above 126 mg/dL or a random blood glucose above 200 mg/dL.
Symptoms
- Excessive thirst (polydipsia)
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Increased hunger (polyphagia)
- Fatigue or weakness
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds or infections
- Unexplained weight loss (in uncontrolled diabetes)
Severe hyperglycaemia may lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state (HHS), both of which are medical emergencies.
Causes
- Diabetes mellitus (Type 1, Type 2, Gestational)
- Skipping or inadequate diabetes medication
- Poor dietary habits (high sugar/carbohydrate intake)
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Stress or illness (infection, surgery, trauma)
- Certain medications (steroids, beta-blockers, diuretics)
- Endocrine disorders (Cushing’s syndrome, hyperthyroidism)
Risk Factors
- Family history of diabetes
- Overweight or obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Unhealthy diet
- Advanced age
- Hypertension and high cholesterol
- History of gestational diabetes
Complications
If left untreated, chronic hyperglycaemia can lead to:
- Cardiovascular disease (heart attack, stroke)
- Diabetic retinopathy (vision loss)
- Diabetic nephropathy (kidney failure)
- Peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage)
- Diabetic foot ulcers
- Increased susceptibility to infections
Prevention
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein
- Regular physical activity (at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week)
- Routine blood sugar monitoring
- Adhering to prescribed medications or insulin therapy
- Regular medical checkups and screening in Korean hospitals
- Stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, or counseling
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Blood glucose tests: Fasting blood sugar, random glucose, and HbA1c test
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) for diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Widely available in Korea, particularly for Type 1 and advanced Type 2 diabetes patients
Medical Treatments
- Oral antidiabetic medications: Metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists
- Insulin therapy: Basal, bolus, or mixed insulin regimens tailored to patient needs
- Emergency management: IV insulin and fluids for diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar state
Lifestyle & Supportive Care
- Dietary management: Nutrition counseling by certified dietitians in Korea
- Exercise programs: Hospital-based diabetes centers provide tailored exercise plans
- Digital health tools: Mobile apps and telemedicine platforms widely used in Korea for glucose monitoring and patient education
Rehabilitation and Long-Term Care
- Regular follow-up with endocrinologists in Korean hospitals like Seoul National University Hospital, Asan Medical Center, and Samsung Medical Center
- Patient education programs for self-care and complication prevention
- Multidisciplinary approach involving ophthalmologists, nephrologists, and cardiologists for long-term management