Overview
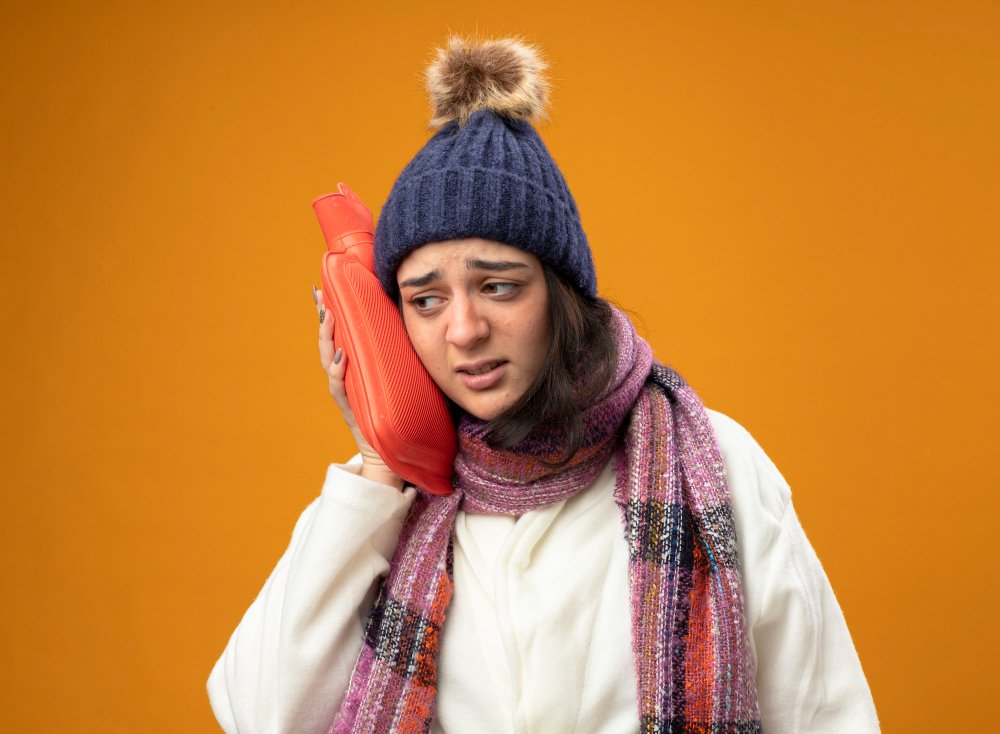
Hypothermia is a medical emergency that occurs when the body loses heat faster than it can produce it, causing the core body temperature to drop below 35°C (95°F). Severe hypothermia can lead to organ failure, cardiac arrest, and death if not treated promptly.
In Korea, hypothermia cases are most commonly seen during harsh winter months in northern regions or among individuals exposed to cold water, outdoor activities, or inadequate heating. Korean hospitals are equipped with emergency response systems, advanced warming therapies, and intensive care units to manage hypothermia efficiently. Public awareness campaigns also emphasize prevention in high-risk populations.
What is Hypothermia?
Hypothermia occurs when the body is unable to maintain its normal temperature due to prolonged exposure to cold. It affects all organ systems, especially the cardiovascular and nervous systems, and can be life-threatening without immediate treatment.
Symptoms
- Shivering (initially)
- Slow, shallow breathing
- Weak pulse
- Confusion or memory loss
- Drowsiness or fatigue
- Slurred speech
- Loss of coordination
- Pale or blue skin
- Severe cases: unconsciousness or cardiac arrest
Causes
- Prolonged exposure to cold weather
- Immersion in cold water
- Wearing inadequate clothing in cold environments
- Alcohol or drug use, which impairs heat regulation
- Certain medical conditions (e.g., hypothyroidism, diabetes, malnutrition)
- Advanced age, which reduces the body’s ability to regulate temperature
Risk Factors
- Elderly individuals with decreased thermoregulation
- Infants and young children
- Homeless or outdoor workers
- Winter sports enthusiasts or mountaineers
- People with chronic medical conditions
- Alcohol or sedative use
Complications
- Frostbite (damage to extremities)
- Hypothermic shock leading to heart arrhythmias
- Organ failure (heart, kidneys, liver)
- Coma or death if untreated
Prevention
- Wearing appropriate layered clothing in cold weather
- Avoiding prolonged exposure to cold and wet conditions
- Keeping homes adequately heated during winter
- Staying dry and avoiding alcohol in cold environments
- Educating outdoor workers and winter sports participants about hypothermia
Treatment Options in Korea
Diagnosis
- Measurement of core body temperature (rectal or esophageal probes)
- Blood tests to monitor electrolytes, glucose, and organ function
- ECG monitoring for cardiac arrhythmias
- Assessment of hypothermia severity (mild, moderate, severe)
Medical Treatments
- Active external rewarming: Heated blankets, warm water bottles, radiant heat
- Active internal rewarming: Warm IV fluids, warmed humidified oxygen, and in severe cases, extracorporeal blood warming
- Supportive care: Oxygen therapy, monitoring for cardiac arrhythmias, and treatment of coexisting conditions
- Medications if necessary to manage complications such as arrhythmias
Rehabilitation and Support
- Gradual warming and monitoring until stable
- Treatment of frostbite or tissue damage
- Counseling and support for high-risk groups (elderly, outdoor workers)
- Public health programs for winter safety awareness