What it is
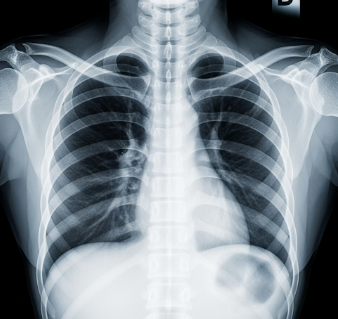
An X-ray is a medical imaging technique that uses electromagnetic radiation to produce images of the inside of the body, primarily to evaluate bones, joints, and certain internal organs.
➡ Key facts:
- ✔ X-rays are quick, painless, and non-invasive
- ✔ Can detect fractures, infections, tumors, and foreign objects
- ✔ Common types include:
- Chest X-ray → Lungs, heart, ribs
- Bone X-ray → Fractures, bone density
- Dental X-ray → Teeth and jaw
- ✔ Available in hospitals, clinics, diagnostic imaging centers, and specialized radiology departments in Korea
💡 X-rays are a fundamental diagnostic tool used in medical, dental, and orthopedic care, guiding treatment and surgical planning.
Why it’s done
X-rays are performed to:
➤ Diagnose fractures and bone injuries → Detect broken or dislocated bones
➤ Evaluate chest conditions → Pneumonia, lung infection, tuberculosis, or heart enlargement
➤ Monitor disease progression → Osteoporosis, arthritis, or cancer
➤ Guide medical procedures → Placement of catheters, pacemakers, or surgical instruments
➤ Detect foreign objects → Swallowed items, shrapnel, or dental issues
⚠ X-rays provide critical diagnostic information, allowing timely and accurate treatment.
Alternatives / Complementary Measures
Other imaging techniques include:
✔ CT scan (Computed Tomography) → More detailed cross-sectional imaging
✔ MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) → Soft tissue imaging without radiation
✔ Ultrasound → Real-time imaging, especially for abdominal or obstetric evaluation
✔ Bone scan or nuclear imaging → For metabolic or cancer evaluation
✔ Fluoroscopy → Real-time moving X-ray for procedures
⚠ Choice depends on clinical need, detail required, and radiation exposure considerations.
Preparation
Before an X-ray in Korea:
🔹 Medical history review → Pregnancy, previous imaging, allergies to contrast (if used)
🔹 Remove metal objects → Jewelry, belts, or removable dental appliances
🔹 Fasting or special preparation → Only needed for certain contrast studies
🔹 Protective measures → Lead aprons or shields for sensitive areas
🔹 Provide prior images → Helpful for comparison
💡 Korean radiology centers provide clear instructions and guidance to ensure accurate imaging and safety.
How it’s done
➡ Step-by-step procedure:
- Positioning → Patient stands, sits, or lies down depending on X-ray type
- Exposure → X-ray beam directed at the target area for a few seconds
- Image capture → Digital or film-based image recorded
- Multiple views → Front, side, or oblique projections for comprehensive assessment
- Completion → Usually takes 5–15 minutes, depending on complexity
💡 The procedure is painless, quick, and requires minimal patient cooperation, with radiographers ensuring proper positioning for accurate results.
Effectiveness & Success Rate
✔ Highly effective for bone and chest evaluation
✔ Immediate results in many clinics with digital X-ray technology
✔ Guides clinical decisions such as casting, surgery, or medication
✔ Reduces need for invasive procedures when diagnosis is clear
💡 Korean hospitals employ modern digital X-ray machines, producing high-resolution images with low radiation exposure.
Recovery / Expected Outcomes
✔ No recovery needed → X-rays are non-invasive and cause no tissue trauma
✔ Immediate feedback → Radiologist reviews images and provides reports
✔ Follow-up imaging → Sometimes needed to monitor healing or disease progression
✔ Safe for repeat use → When clinically necessary, with radiation exposure minimized
💡 Patients often resume normal activities immediately after the procedure.
Complications / Risks
⚠ X-rays are generally safe, but potential risks include:
➡ Radiation exposure → Low doses in diagnostic imaging; cumulative exposure monitored
➡ Pregnancy concerns → Risk to the fetus; alternative imaging may be preferred
➡ Contrast reactions → Rare, only if contrast dye is used for specialized studies
➡ Allergic reactions → Extremely rare
💡 Korean imaging centers adhere to ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principles, minimizing radiation while ensuring diagnostic quality.
Treatment Options in Korea (Post-X-ray Care)
🔹 No recovery interventions needed → Non-invasive procedure
🔹 Report review → Radiologist provides findings to the referring doctor
🔹 Follow-up imaging → If fracture healing, disease progression, or pre/post-treatment monitoring is required
🔹 Additional tests → CT, MRI, or ultrasound if more detail is needed
🔹 Patient counseling → Explanation of findings and recommended next steps
💡 Korean hospitals provide integrated radiology services, allowing seamless care from imaging to treatment planning.
Top Hospitals & Clinics in Korea for X-ray
🏥 Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Advanced diagnostic imaging and radiology services
🏥 Asan Medical Center (Seoul) – State-of-the-art X-ray, CT, and digital imaging
🏥 Samsung Medical Center (Seoul) – Comprehensive imaging for bone, chest, and dental evaluation
🏥 Yonsei Severance Hospital – Integrated radiology services with expert interpretation
🏥 Private diagnostic centers nationwide – Accessible, quick, and digital imaging solutions
Conclusion
X-ray in Korea is a safe, fast, and essential diagnostic tool for evaluating bones, chest, dental, and other areas.
✔ Provides critical information for diagnosis and treatment planning
✔ Quick, non-invasive, and generally requires no recovery time
✔ Minimal risks with modern digital imaging and protective measures
✔ Korean hospitals offer expert radiologists, advanced equipment, and integrated care
By combining modern X-ray technology, skilled radiographers, and comprehensive diagnostic services, Korea ensures accurate results, patient safety, and efficient clinical care.