What it is
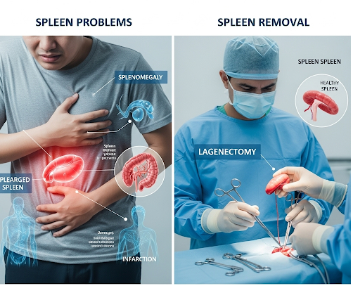
The spleen is an organ located in the upper left abdomen that plays a crucial role in filtering blood, recycling red blood cells, and supporting the immune system.
➡ Spleen problems may include:
- Enlargement (splenomegaly)
- Rupture due to trauma
- Blood disorders (like anemia or thrombocytopenia)
- Cysts, abscesses, or tumors
When the spleen is severely damaged or diseased, spleen removal (splenectomy) may be necessary.
💡 In Korea, spleen evaluation, treatment, and surgical removal are available at most tertiary hospitals and specialized surgical centers.
Why it’s done
Doctors recommend evaluation or removal of the spleen for:
➤ Trauma or rupture → Life-threatening bleeding from accidents or injuries
➤ Blood disorders → Low platelet counts, hemolytic anemia, or certain cancers
➤ Enlargement causing symptoms → Pain, early satiety, or pressure on other organs
➤ Infections or cysts → Abscesses or non-functioning spleen
➤ Cancer involvement → Lymphoma, leukemia, or metastasis
⚠ Untreated spleen problems can lead to severe bleeding, infection, or life-threatening complications.
Alternatives
Depending on the condition, alternatives to splenectomy include:
✔ Medication and monitoring → For mild enlargement or blood disorders
✔ Partial splenectomy → Preserves some spleen function while removing damaged portion
✔ Minimally invasive drainage → For cysts or abscesses
✔ Supportive therapy → Blood transfusions, antibiotics, or immune modulation
⚠ In traumatic rupture or severe disease, complete removal is often the safest option.
Preparation
Before a spleen removal procedure in Korea:
🔹 Medical evaluation → Blood tests, imaging (CT or ultrasound), and physical exam
🔹 Vaccinations → Recommended against pneumococcus, meningococcus, and Haemophilus influenzae type b before surgery to prevent post-splenectomy infections
🔹 Medication review → Adjust anticoagulants, aspirin, or other blood-thinning drugs
🔹 Fasting → Usually 6–8 hours before surgery
🔹 Consent and counseling → Risks, recovery, and lifestyle changes explained
💡 Korean hospitals also provide preoperative patient education and psychological support for splenectomy.
How it’s done
➡ Step-by-step process of spleen removal (splenectomy) in Korea:
- Anesthesia → General anesthesia administered
- Surgical approach:
- Laparoscopic splenectomy → Small incisions, camera-guided, shorter recovery
- Open splenectomy → Larger incision, preferred for trauma or very large spleens
- Organ removal → Surgeon removes spleen carefully to prevent bleeding
- Closure → Incisions closed, drains placed if necessary
- Recovery in hospital → Typically 2–7 days, depending on surgical method and patient condition
💡 Laparoscopic splenectomy is increasingly preferred in Korea due to less pain, faster recovery, and lower complication rates.
Effectiveness & Success Rate
✔ Splenectomy is highly effective for controlling:
- Severe blood disorders
- Traumatic spleen rupture
- Symptomatic splenomegaly
✔ Mortality rate is low in Korea (<1%) when performed in tertiary hospitals
✔ Postoperative quality of life is generally good, with precautions against infection
Recovery / Expected Outcomes
✔ Hospital stay → 2–7 days for uncomplicated cases
✔ Return to normal activities → Within 2–4 weeks for laparoscopic surgery; 6–8 weeks for open surgery
✔ Diet and activity → Gradual resumption; avoid heavy lifting early
✔ Vaccinations and antibiotics → Long-term preventive measures against infections
✔ Follow-up → Regular check-ups, blood tests, and imaging if underlying disease exists
Complications / Risks
⚠ Surgery-related risks
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Injury to surrounding organs (stomach, pancreas, colon)
⚠ Post-splenectomy risks
- Increased susceptibility to infections (overwhelming post-splenectomy infection, OPSI)
- Blood clots
- Rare long-term immune deficiencies
💡 In Korea, hospitals mitigate risks by:
- Preoperative vaccines
- Prophylactic antibiotics for high-risk patients
- Patient education on early recognition of infection
Treatment Options in Korea (Post-Splenectomy Care)
🔹 Medical monitoring → Blood counts, immune status, and liver function tests
🔹 Vaccinations → Pneumococcal, meningococcal, and Hib vaccines recommended
🔹 Antibiotic prophylaxis → Especially in children and immunocompromised adults
🔹 Lifestyle and education → Avoiding high-risk exposure to infections; prompt medical attention for fever
🔹 Management of underlying conditions → Hematology, oncology, or infectious disease follow-up
Top Hospitals & Clinics in Korea for Spleen Surgery
🏥 Asan Medical Center (Seoul) – Advanced laparoscopic and open splenectomy
🏥 Samsung Medical Center – Tertiary care for trauma-related spleen injuries
🏥 Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Expertise in blood disorders and spleen surgery
🏥 Yonsei Severance Hospital – Hematology-focused splenectomy care
🏥 Regional tertiary hospitals – Offer emergency spleen surgery for trauma cases
Conclusion
Spleen problems and spleen removal in Korea involve comprehensive care from diagnosis to post-surgical follow-up.
✔ Splenectomy is effective for trauma, blood disorders, and symptomatic enlargement
✔ Laparoscopic techniques provide faster recovery and less pain
✔ Post-splenectomy vaccination and preventive care are critical to reduce infection risk
✔ Korean hospitals provide world-class surgical care, patient education, and long-term follow-up
By addressing spleen issues promptly, patients in Korea can recover fully and maintain a healthy lifestyle, even after splenectomy.