What it is
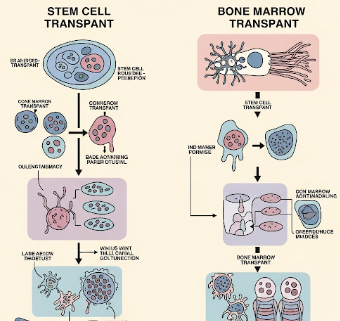
Stem cell and bone marrow transplants are advanced medical procedures used to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy stem cells, which can regenerate the patient’s blood and immune system.
➡ Key facts:
- ✔ Used to treat blood disorders, cancers, and certain genetic diseases.
- ✔ Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside bones that produces blood cells.
- ✔ Stem cells can come from the patient (autologous), a donor (allogeneic), or cord blood.
- ✔ In Korea, these transplants are available at major hospitals with specialized hematology and oncology units, following strict international protocols.
💡 These transplants are life-saving procedures for conditions such as leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma, aplastic anemia, and inherited immune deficiencies.
Why it’s done
Doctors recommend stem cell or bone marrow transplants for:
➤ Blood cancers → Leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma
➤ Severe anemia → Aplastic anemia, thalassemia
➤ Inherited disorders → Immune deficiencies, metabolic diseases
➤ Chemotherapy or radiation support → To restore blood and immune cells after high-dose therapy
➤ Relapsed or refractory disease → When standard treatments fail
⚠ Without transplantation, many of these conditions can be fatal or lead to severe complications.
Alternatives
Depending on the disease, alternatives may include:
✔ Chemotherapy or radiation alone → Often used before or instead of transplant for certain cancers
✔ Immunotherapy → CAR-T cell therapy or monoclonal antibodies for hematologic malignancies
✔ Supportive care → Blood transfusions, medications, and infection prevention
✔ Gene therapy → Experimental treatment for certain inherited disorders
⚠ While alternatives can help manage symptoms or disease progression, only stem cell or bone marrow transplant can provide long-term cure in many cases.
Preparation
Before a transplant in Korea:
🔹 Medical evaluation → Comprehensive blood tests, imaging, heart and lung function assessment
🔹 Donor matching → HLA (human leukocyte antigen) matching for allogeneic transplants
🔹 Pre-transplant conditioning → Chemotherapy and/or radiation to destroy diseased marrow
🔹 Vaccinations and infection control → Minimize infection risk
🔹 Psychological preparation → Counseling to manage stress and expectations
💡 Korean hospitals provide detailed pre-transplant education for patients and families, including lifestyle changes and isolation protocols.
How it’s done
➡ Step-by-step process in Korea:
- Stem cell collection
- Autologous → Collected from patient’s own blood or marrow
- Allogeneic → Collected from matched donor (bone marrow or peripheral blood)
- Conditioning therapy → High-dose chemotherapy/radiation to destroy diseased marrow
- Transplantation → Stem cells infused through intravenous line
- Engraftment and monitoring → Stem cells migrate to bone marrow and begin producing blood cells
- Hospital stay → Typically 3–6 weeks depending on complications and recovery
- Post-transplant care → Immunosuppressants (for allogeneic) and infection prevention
💡 Advanced centers in Korea use state-of-the-art isolation units and monitoring technology to ensure patient safety during the critical post-transplant period.
Effectiveness & Success Rate
✔ Autologous transplant:
- High success in multiple myeloma and lymphoma
- Low risk of rejection since patient’s own cells are used
✔ Allogeneic transplant:
- Can cure certain leukemias and genetic disorders
- Success depends on HLA match, age, and overall health
- Complications such as graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) are managed proactively
✔ Survival rates in Korea:
- 3–5 year survival: 50–70% for leukemia and lymphoma, depending on patient age and disease stage
- Infection and GVHD management protocols significantly improve outcomes
Recovery / Expected Outcomes
✔ Initial recovery occurs in hospital over 3–6 weeks
✔ Full immune system recovery may take 6–12 months
✔ Patients may experience:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Risk of infections
- Graft-versus-host disease (for allogeneic transplants)
✔ Follow-up involves: - Regular blood tests
- Bone marrow monitoring
- Adjustment of medications, especially immunosuppressants
Complications / Risks
⚠ Stem cell and bone marrow transplants are high-risk procedures. Potential complications include:
➡ Short-term risks:
- Infection due to weakened immunity
- Bleeding or anemia
- Organ toxicity from chemotherapy/radiation
➡ Long-term risks:
- Graft-versus-host disease (allogeneic)
- Relapse of original disease
- Chronic infections or immune dysfunction
💡 In Korea, advanced supportive care, infection control, and experienced transplant teams minimize these risks.
Treatment Options in Korea (Post-Transplant Care)
🔹 Hospital monitoring → Continuous monitoring during the critical first month
🔹 Medications → Immunosuppressants, antivirals, antibiotics, and antifungals
🔹 Rehabilitation → Nutritional support, physical therapy, psychological support
🔹 Vaccinations → Re-immunization to rebuild immunity post-transplant
🔹 Long-term follow-up → Blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and infection surveillance
💡 Korean transplant centers also provide remote monitoring, telemedicine support, and patient education for post-discharge care.
Top Hospitals & Clinics in Korea for Stem Cell/Bone Marrow Transplants
🏥 Samsung Medical Center (Seoul) – Leading hematology and transplant center
🏥 Asan Medical Center (Seoul) – Advanced isolation and transplant facilities
🏥 Seoul National University Hospital (SNUH) – Expertise in leukemia, lymphoma, and genetic disorders
🏥 Yonsei Severance Hospital – Specialized in allogeneic and autologous transplants
🏥 CHA Bundang Medical Center – Pediatric stem cell transplant programs
Conclusion
Stem cell and bone marrow transplants in Korea are life-saving procedures for patients with blood cancers, genetic disorders, and severe hematologic diseases.
✔ Provides potential long-term cure when other treatments fail
✔ Supported by highly specialized hospitals and experienced medical teams
✔ Post-transplant care, vaccinations, and infection control are rigorously managed
✔ Korean patients benefit from advanced technology, strict protocols, and comprehensive follow-up
By offering world-class transplantation programs, Korea ensures that patients have access to cutting-edge treatments with the best possible outcomes.