What it is
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment that involves placing specially prepared sperm directly into a woman’s uterus during ovulation to increase the chance of pregnancy. This minimally invasive procedure is often the first-line fertility treatment for couples experiencing difficulty conceiving.
Key points:
- Also called artificial insemination.
- Performed during a woman’s fertile window for maximum effectiveness.
- Sperm is washed and concentrated to remove impurities and improve motility.
- Less invasive and lower cost compared to in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Why it’s done
IUI is recommended for a variety of fertility issues:
- Mild male infertility: Low sperm count or reduced motility.
- Cervical factors: Problems with cervical mucus that prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
- Unexplained infertility: When no clear cause is identified after evaluation.
- Ovulation disorders: Women with irregular or absent ovulation may combine IUI with fertility medications.
- Single women or same-sex couples: Using donor sperm to achieve pregnancy.
- Couples with sexual difficulties: In cases of erectile dysfunction or inability to have intercourse.
Note: IUI is often used as a first-line treatment before considering more complex procedures like IVF.
Alternatives
Other fertility treatment options include:
- Timed intercourse: Natural conception during the fertile window with monitoring.
- Ovulation induction with medications: To stimulate egg release before intercourse or IUI.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): Fertilization occurs outside the body before embryo transfer.
- Donor sperm or egg programs: When one partner has fertility challenges.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI): Direct injection of a sperm into an egg, used for severe male infertility.
Important: The choice of treatment depends on fertility diagnosis, age, and previous treatment attempts.
Preparation
Proper preparation improves the success rate and safety of IUI:
- Fertility evaluation: Blood tests, ultrasound, semen analysis, and hormone assessment.
- Ovulation monitoring: Tracking follicle development and timing insemination with ovulation detection kits or ultrasound.
- Sperm preparation: Sperm is collected and washed to concentrate motile sperm and remove seminal plasma.
- Medication: Some women may receive ovulation-stimulating drugs to increase success rates.
- Informed consent: Understanding procedure steps, risks, and success rates.
Patient instructions:
- Abstain from sexual intercourse for 2–5 days prior to sperm collection.
- Follow medication or monitoring schedule provided by the fertility clinic.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: balanced diet, no smoking or excessive alcohol, and moderate exercise.
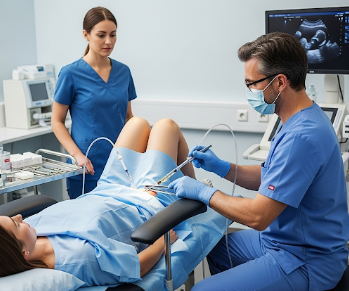
How it’s done
IUI is a relatively quick, outpatient procedure:
- Sperm preparation: Sperm is washed and concentrated in the lab.
- Patient positioning: Woman lies on an exam table similar to a gynecologic exam.
- Catheter insertion: A thin, flexible catheter is gently inserted through the cervix into the uterus.
- Sperm placement: The prepared sperm is introduced into the uterus near the time of ovulation.
- Completion: Catheter is removed, and the patient rests briefly before leaving the clinic.
Duration: Usually 5–15 minutes. Minimal discomfort is expected.
Success rates:
- Vary depending on age, fertility diagnosis, and use of ovulation-stimulating medications.
- Typically ranges from 10–20% per cycle.
Recovery / Post-Procedure Considerations
Recovery from IUI is usually rapid and uncomplicated:
- Activity: Normal activities can be resumed immediately. Light cramping may occur.
- Pregnancy testing: Blood test or urine test 2 weeks after IUI to confirm pregnancy.
- Follow-up: Clinic may schedule ultrasound or hormone monitoring if pregnancy occurs.
- Emotional support: Coping with uncertainty and potential stress is important for patient well-being.
Benefits of correct use:
- Minimally invasive and relatively low-risk fertility option.
- Can be repeated over several cycles if unsuccessful initially.
- Allows for timed fertilization in a controlled environment.
Complications / Risks
IUI is generally safe but may involve minor risks:
- Mild cramping or spotting: Due to catheter insertion.
- Infection: Rare, but preventive measures and hygiene reduce risk.
- Multiple pregnancy: Higher chance if ovulation-inducing drugs are used.
- Emotional stress: Anxiety or disappointment if cycles are unsuccessful.
Prevention:
- Use sterile techniques during the procedure.
- Follow clinic instructions for medications and post-procedure care.
- Limit repeated attempts to prevent ovarian overstimulation.
Treatment Options in Korea
IUI is widely available in fertility clinics and hospitals across Korea:
Key features:
- Offered in public and private fertility centers with advanced reproductive technologies.
- Combination with ovulation induction or donor sperm programs available.
- Experienced fertility specialists provide personalized protocols, monitoring, and counseling.
- High-quality laboratory facilities ensure sperm preparation and handling meet international standards.
- Post-procedure support includes pregnancy monitoring, emotional counseling, and follow-up care.
Summary: Intrauterine insemination (IUI) in Korea is a safe, minimally invasive, and effective fertility treatment for couples or individuals facing reproductive challenges. With proper evaluation, precise timing, and professional care, IUI offers a valuable first-line option for achieving pregnancy.