What it is
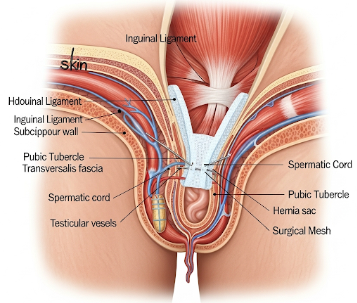
An inguinal hernia occurs when tissue, such as part of the intestine or fatty tissue, protrudes through a weak spot in the lower abdominal wall near the groin. It is one of the most common types of hernias and is more prevalent in men, though women can also develop them.
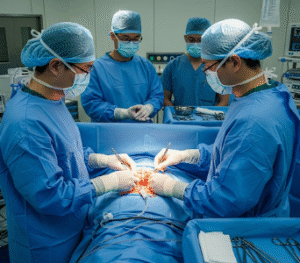
Inguinal hernia repair is a surgical procedure designed to return the herniated tissue to its proper place and strengthen the abdominal wall to prevent recurrence. The repair can be performed through open surgery or minimally invasive laparoscopic techniques, often using a surgical mesh to reinforce the weak area.
Key points:
- Corrects herniated tissue in the inguinal canal.
- Prevents complications such as incarceration or strangulation.
- Can be performed electively or in emergency situations.
Why it’s done
Inguinal hernia repair is performed for several reasons:
- Symptomatic relief: Pain, swelling, or discomfort in the groin, especially during physical activity.
- Prevent complications: Incarceration (trapped tissue) or strangulation (cut-off blood supply) can lead to emergent medical conditions.
- Elective correction: To improve quality of life and prevent chronic discomfort.
- Long-term prevention: Reduces the likelihood of hernia enlargement and future complications.
Note: Hernias rarely resolve on their own, making surgical intervention the definitive treatment.
Alternatives
While surgery is the standard, alternatives are limited and often temporary:
- Watchful waiting: May be considered for small, asymptomatic hernias, but carries the risk of sudden complications.
- Truss or support garments: Provide temporary relief but do not repair the hernia.
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding heavy lifting or straining may reduce discomfort but cannot eliminate the hernia.
Important: Non-surgical management is generally not recommended for inguinal hernias at risk of strangulation.
Preparation
Proper preparation helps ensure surgical safety and optimal outcomes:
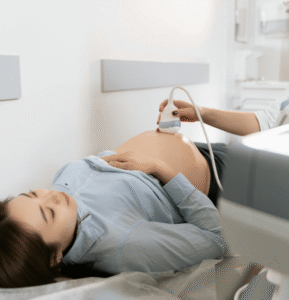
- Medical evaluation: Blood tests, ECG, imaging (ultrasound or CT scan) to assess hernia size and location.
- Medication review: Inform the surgeon about anticoagulants, aspirin, or other medications.
- Fasting: Typically 6–8 hours before surgery for procedures under general anesthesia.
- Bowel preparation: Sometimes recommended for laparoscopic repair.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Stop smoking and ensure good hydration to promote healing.
Patient instructions:
- Arrange post-surgery transportation and support at home.
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing on the day of surgery.
- Adhere strictly to preoperative instructions provided by the surgeon.
How it’s done
Inguinal hernia repair can be performed using two main approaches:
1. Open Inguinal Hernia Repair:
- A small incision is made over the groin.
- Herniated tissue is gently reduced back into the abdominal cavity.
- The hernia defect is closed and reinforced with mesh or sutures.
- Skin is closed, and a sterile dressing is applied.
2. Laparoscopic (Minimally Invasive) Repair:
- Small incisions are made in the abdominal wall.
- A laparoscope and surgical instruments are used to reduce the hernia and place a mesh.
- Benefits include less postoperative pain, faster recovery, and minimal scarring.
Considerations:
- The choice of method depends on hernia size, recurrence, patient health, and surgeon expertise.
- Mesh repair is often preferred due to lower recurrence rates, though tissue-only repair may be performed in select cases.
Recovery
Recovery depends on surgical technique and individual health:
Immediate post-surgery:
- Mild to moderate groin pain is common; painkillers are prescribed as needed.
- Walking is encouraged within hours to prevent blood clots.
- Hospital stay ranges from same-day discharge (laparoscopic) to 1–2 days (open surgery).
First 2–4 weeks:
- Avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activity.
- Swelling and bruising are normal but decrease over time.
- Follow-up visits ensure proper healing and early detection of complications.
Long-term recovery:
- Most patients resume normal activities within 2–6 weeks.
- Recurrence risk is low with mesh repair.
- Maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding straining reduces long-term risk.
Complications
Though generally safe, inguinal hernia repair can involve risks:
- Infection: At incision or surgical site.
- Bleeding or hematoma: Blood accumulation under the skin.
- Nerve injury: May cause temporary numbness or groin discomfort.
- Recurrence: More likely with tissue-only repair.
- Chronic groin pain: Can occur in some cases.
- Anesthesia-related risks: Including nausea, allergic reactions, or cardiovascular events (rare).
Preventive measures:
- Choose a qualified surgeon with experience in hernia repair.
- Follow postoperative care instructions carefully.
- Report persistent pain, fever, or swelling promptly.
Treatment Options in Korea
In Korea, inguinal hernia repair is widely available and highly effective:
Features of treatment in Korea:
- Performed in general hospitals, surgical centers, and specialized hernia clinics.
- Both open and laparoscopic techniques are routinely used.
- Focus on minimally invasive approaches for faster recovery and reduced postoperative pain.
- Preoperative evaluation includes advanced imaging and laboratory tests.
- Postoperative care involves pain management, wound care, and rehabilitation guidance.
Korean hospitals follow international surgical standards, ensuring high success rates and patient safety. Patients can expect modern facilities, experienced surgeons, and structured follow-up care for optimal outcomes.
Summary: Inguinal hernia repair in Korea is a safe and effective procedure that restores abdominal wall integrity, prevents serious complications, and allows patients to return to normal activity. Proper diagnosis, preparation, and post-surgical care contribute to successful recovery and minimal risk of recurrence.