What it is
Hip replacement, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which a damaged or diseased hip joint is replaced with an artificial joint (prosthesis). This procedure is commonly recommended for individuals suffering from severe osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, hip fractures, or avascular necrosis, which cause chronic pain, reduced mobility, and impaired quality of life.
Key points:
- Can be total hip replacement (both ball and socket replaced) or partial hip replacement (only one part replaced).
- The prosthetic joint can be made from metal, ceramic, or high-grade plastic materials.
- The goal is to relieve pain, restore function, and improve mobility.
- Typically performed under general or spinal anesthesia.
Why it’s done
Hip replacement is indicated for patients with:
- Severe arthritis: Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis causing persistent pain and stiffness.
- Hip fractures: Especially in older adults where the joint is irreparably damaged.
- Avascular necrosis: Death of bone tissue due to disrupted blood supply.
- Reduced mobility and daily function: Interference with walking, climbing stairs, or performing routine activities.
- Failure of conservative treatments: Such as physical therapy, medications, or injections that no longer relieve symptoms.
Note: Hip replacement is considered when pain and disability significantly affect quality of life.
Alternatives
Before surgery, several non-surgical options may be considered:
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and corticosteroid injections.
- Physical therapy: Strengthening muscles around the hip to improve function.
- Lifestyle modifications: Weight management, activity adjustments, and mobility aids.
- Hip resurfacing: Preserves more of the patient’s bone, often recommended for younger patients.
- Assistive devices: Canes, walkers, or crutches to reduce joint stress.
Important: These alternatives may reduce symptoms temporarily but do not correct joint damage. Surgery is usually required for long-term relief.
Preparation
Preparation ensures safe surgery and optimal outcomes:
- Medical evaluation: Blood tests, ECG, chest X-ray, and imaging (X-ray or MRI) of the hip joint.
- Medication review: Inform the surgeon of all medications, including blood thinners and supplements.
- Preoperative exercises: Strengthening surrounding muscles may speed recovery.
- Weight management: Reducing excess weight minimizes stress on the new joint.
- Fasting: Typically required 6–8 hours before surgery for general anesthesia.
- Home preparation: Arrange for post-surgery support, mobility aids, and a safe environment.
How it’s done
Hip replacement can be performed using different surgical approaches:
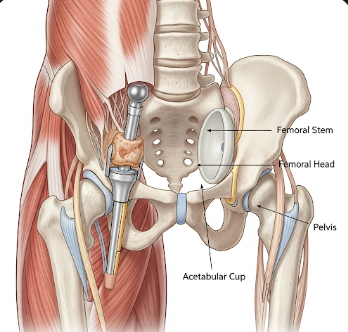
1. Total Hip Replacement (THR):
- Damaged femoral head and socket are removed.
- A metal or ceramic prosthetic ball replaces the femoral head.
- A plastic or ceramic socket is inserted into the pelvic bone.
- The prosthesis may be cemented or cementless, depending on bone quality.
2. Partial Hip Replacement:
- Only the femoral head is replaced, typically in hip fractures in older adults.
- The natural socket is left intact.
Surgical approaches include:
- Posterior approach: Access from the back of the hip; most common.
- Anterior approach: Access from the front; allows faster recovery and fewer restrictions on movement.
- Lateral approach: Side of the hip; may reduce risk of dislocation.
Procedure duration: Typically 1–2 hours, with anesthesia and post-surgical recovery extending total time.
Recovery
Recovery varies based on surgical approach, patient health, and adherence to rehabilitation:
Immediate post-surgery:
- Pain and swelling are managed with medications.
- Physical therapy begins within 24 hours, focusing on gentle movements and walking with support.
- Hospital stay usually ranges from 2–5 days.
First 6–12 weeks:
- Gradual increase in walking, climbing stairs, and low-impact activities.
- Physical therapy focuses on strength, balance, and mobility.
- Use of walking aids (walker, cane) decreases over time.
Long-term recovery:
- Full recovery may take 3–6 months for most patients.
- Most patients can resume daily activities and light exercise.
- High-impact activities (running, jumping) are usually discouraged to preserve the prosthesis.
Complications
Hip replacement is generally safe, but potential risks include:
- Infection: At the surgical site or deep joint infection.
- Blood clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism.
- Dislocation: Especially in the early post-surgery period.
- Leg length discrepancy: Minor differences are common; severe cases may need correction.
- Loosening or wear of the prosthesis: May require revision surgery in the long term.
- Nerve or blood vessel injury: Rare but possible.
- Pain or stiffness: May persist if rehabilitation is inadequate.
Prevention:
- Follow all postoperative instructions, including physical therapy.
- Use blood-thinning medications if prescribed.
- Avoid movements that risk dislocation during early recovery.
Treatment Options in Korea
Hip replacement in Korea is a widely performed and advanced procedure:
Features of hip replacement in Korea:
- Available in general hospitals, orthopedic specialty centers, and university hospitals.
- Both traditional and minimally invasive surgical approaches are offered.
- High standards of preoperative evaluation, surgical precision, and post-operative rehabilitation.
- Use of modern prosthetic materials with long-term durability.
- Structured rehabilitation programs to ensure optimal recovery and mobility restoration.
Patients can expect safe, effective surgery with high success rates, allowing them to resume daily activities, improve quality of life, and reduce chronic pain.
Summary: Hip replacement in Korea is a proven solution for severe hip joint damage, offering pain relief, restored mobility, and improved function. With proper preoperative preparation, surgical expertise, and post-surgical rehabilitation, patients can achieve excellent long-term outcomes.