What it is
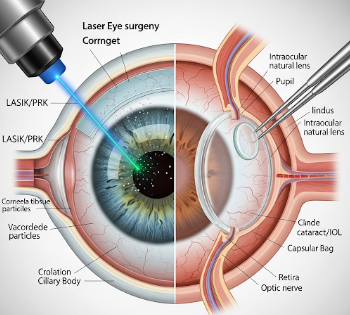
Laser eye surgery and lens surgery are procedures designed to correct refractive errors and improve vision.
Laser Eye Surgery:
- Uses precise lasers to reshape the cornea, correcting myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism.
- Common procedures include LASIK, PRK, and LASEK.
Lens Surgery:
- Involves removing the eye’s natural lens and replacing it with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
- Often performed to treat cataracts or severe refractive errors.
- Types of lens surgery include cataract surgery, refractive lens exchange (RLE), and phakic IOL implantation.
Key points:
- Both procedures aim to reduce dependence on glasses or contact lenses.
- Typically outpatient procedures with rapid visual recovery.
- High success and satisfaction rates when performed by experienced surgeons.
Why it’s done
These surgeries are indicated for:
Laser Eye Surgery:
- Correct myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
- Reduce dependence on corrective lenses.
- Improve vision quality for sports, driving, or professional needs.
Lens Surgery:
- Remove cataracts causing blurred or cloudy vision.
- Correct high refractive errors not suitable for laser surgery.
- Treat presbyopia using multifocal or accommodating lenses.
Note: Choice of procedure depends on age, eye health, refractive error, and lifestyle needs.
Alternatives
Other options include:
- Glasses or contact lenses: Non-surgical correction.
- Orthokeratology (Ortho-K): Night-time contact lenses that reshape the cornea temporarily.
- Lens-based refractive surgery: Alternative for high prescriptions unsuitable for laser surgery.
- Medication for cataracts: No true alternative; surgery is definitive for lens opacity.
Important: Laser and lens surgery provide long-term vision correction and may be preferred for convenience and lifestyle improvement.
Preparation
Preparation ensures safety and optimal results:
- Comprehensive eye exam: Measures vision, corneal thickness, pupil size, and eye health.
- Medical history review: Includes eye diseases, medications, and systemic conditions.
- Discontinue contact lenses: Typically 2–4 weeks before laser surgery.
- Preoperative instructions: Avoid makeup or lotions on the day of surgery; follow medication guidance.
- Informed consent: Discuss risks, benefits, expected outcomes, and potential complications.
How it’s done
Laser Eye Surgery (LASIK/PRK/LASEK):
- Numbing eye drops are applied.
- A laser reshapes the cornea to correct the refractive error.
- Procedure typically takes 10–20 minutes for both eyes.
- Recovery is rapid; vision often improves within 24–48 hours.
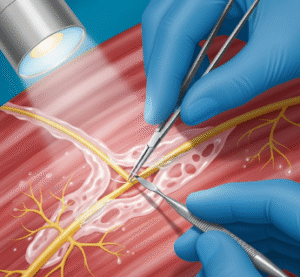
Lens Surgery (Cataract or Refractive Lens Exchange):
- Local anesthesia is applied via eye drops or injection.
- Small incision is made in the cornea.
- Natural lens is removed using ultrasound (phacoemulsification) or laser assistance.
- Artificial intraocular lens (IOL) is inserted.
- Incision is usually self-sealing; stitches are rarely needed.
- Procedure takes 20–45 minutes per eye.
Recovery
Recovery differs slightly depending on the procedure:
Laser Eye Surgery:
- Mild irritation, dryness, or blurred vision initially.
- Avoid rubbing eyes; use prescribed eye drops.
- Most patients return to normal activities within 1–3 days.
Lens Surgery:
- Mild discomfort, watery eyes, or light sensitivity for a few days.
- Use antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops as prescribed.
- Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activity for 1–2 weeks.
- Full visual stabilization usually occurs in 4–6 weeks.
Benefits:
- Significant improvement in vision.
- Reduced dependence on glasses or contacts.
- Quick resumption of daily activities.
Complications / Risks
Both procedures are generally safe, but potential risks include:
Laser Eye Surgery:
- Dry eyes or temporary blurred vision.
- Glare, halos, or night vision issues.
- Overcorrection or undercorrection, sometimes requiring enhancement.
- Rare infections or flap complications.
Lens Surgery:
- Infection or inflammation (endophthalmitis).
- Dislocation of the lens.
- Posterior capsule opacification (secondary cataract).
- Rare retinal detachment or vision loss.
Prevention:
- Performed by experienced ophthalmologists.
- Follow postoperative care instructions carefully.
- Attend all follow-up appointments for monitoring and early intervention.
Treatment Options in Korea
Laser and lens surgeries are widely available in Korean hospitals, specialized eye centers, and ophthalmology clinics:
Key features:
- Advanced laser systems and phacoemulsification equipment.
- Experienced ophthalmologists with high success rates.
- Both refractive and cataract surgeries offered with customized treatment plans.
- Postoperative care includes follow-up exams, eye drops, and patient education.
- Suitable for patients seeking high-quality, precise vision correction with rapid recovery.
Summary: Laser eye surgery and lens surgery in Korea provide safe, effective, and advanced options for vision correction. With modern technology and expert care, patients benefit from improved visual acuity, faster recovery, and reduced dependence on corrective lenses.