What it is
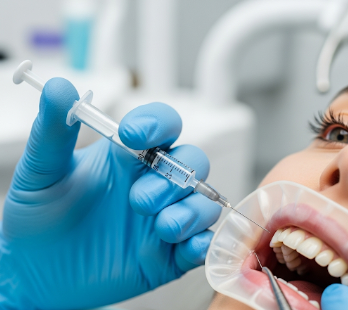
Local anaesthesia is a medical technique in which a specific area of the body is numbed to prevent pain during surgical or diagnostic procedures, without affecting consciousness. Unlike general anaesthesia, patients remain awake and alert while the targeted region is desensitized.
Key points:
- Provides temporary, localized loss of sensation.
- Can be used for minor surgeries, dental procedures, skin treatments, or minor biopsies.
- Administered via injection, topical application, or infiltration around nerves or tissues.
- Generally considered safe with minimal systemic effects compared to general anaesthesia.
Why it’s done
Local anaesthesia is used for procedures that:
- Require pain relief in a small, targeted area (e.g., sutures, mole removal, dental work).
- Allow the patient to remain awake, which may be important for certain diagnostic procedures or intraoperative feedback.
- Reduce risks associated with general anaesthesia, particularly in elderly or medically compromised patients.
- Allow outpatient procedures with rapid recovery and minimal downtime.
Note: It is unsuitable for procedures involving major organs, extensive surgeries, or prolonged operating times.
Alternatives
Alternatives to local anaesthesia include:
- General anaesthesia: Patient is fully unconscious; used for major surgeries.
- Regional anaesthesia: Numbs a larger area, such as an arm or leg (e.g., spinal or epidural anaesthesia).
- Sedation or monitored anaesthesia care: Used in combination with local anaesthesia for anxiolysis or partial sleep.
- Topical analgesics or numbing creams: For minor skin procedures or superficial interventions.
Important: Choice of anaesthesia depends on procedure type, patient health, duration, and surgeon preference.
Preparation
Proper preparation ensures safety and effectiveness:
- Medical history review: Allergies, previous reactions to anaesthetics, medications, and chronic illnesses.
- Fasting: Usually not required for local anaesthesia but may be advised if sedation is used.
- Skin preparation: Clean and disinfect the area where the anaesthetic will be applied.
- Informed consent: Discuss procedure, expected sensation, risks, and duration.
- Medication adjustment: Patients may be advised to stop blood thinners temporarily depending on procedure.
Patient instructions:
- Wear comfortable clothing for easy access to the treatment site.
- Report any history of adverse reactions to local anaesthetics.
- Follow the clinician’s preoperative instructions carefully.
How it’s done
Local anaesthesia is administered in several ways:
- Injection: Anaesthetic solution is injected directly into or around the tissue or nerve supplying the area.
- Topical application: Creams, gels, or sprays are applied to the skin or mucous membranes.
- Infiltration: Anaesthetic is spread into a wider area to cover multiple nerve endings.
- Nerve block: Anaesthetic is injected near a major nerve to numb a larger region (e.g., dental nerve block).
Duration: Onset is typically a few minutes, with numbing lasting 30 minutes to several hours depending on the drug and dose.
Recovery / Post-Procedure Considerations
Recovery from local anaesthesia is generally rapid and uncomplicated:
- Sensation returns gradually as the drug wears off.
- Mild bruising, redness, or swelling may occur at the injection site.
- Normal activities can usually resume within a few hours.
- Follow-up care: If the procedure involved surgery or biopsy, follow instructions regarding wound care, activity restrictions, and pain management.
Benefits:
- Avoids risks of general anaesthesia.
- Enables rapid recovery and same-day discharge.
- Minimal systemic side effects.
Complications / Risks
Local anaesthesia is generally safe but may include:
- Allergic reactions: Rare; symptoms include rash, itching, or swelling.
- Temporary nerve irritation or numbness: Usually resolves within hours to days.
- Injection site complications: Bruising, minor bleeding, or infection.
- Systemic effects: Rare if large doses are used, including dizziness, low blood pressure, or arrhythmias.
Prevention:
- Administered by trained medical professionals.
- Use appropriate dose and injection technique.
- Monitor patients for allergic or systemic reactions.
Treatment Options in Korea
Local anaesthesia is widely available in Korean hospitals, dental clinics, dermatology centers, and outpatient surgical units:
Key features:
- Used for minor surgeries, dental procedures, dermatological treatments, and biopsies.
- Administered by experienced anesthesiologists, surgeons, or trained medical staff.
- Rapid recovery allows same-day discharge for most outpatient procedures.
- Safe and effective for patients who are not candidates for general anaesthesia.
- Suitable for all ages and for patients with underlying medical conditions requiring minimal systemic risk.
Summary: Local anaesthesia in Korea is a safe, effective, and widely used technique for pain management during minor surgical and diagnostic procedures. It offers targeted pain relief, rapid recovery, and minimal systemic side effects, making it an ideal choice for outpatient and minor surgical care.