What it is
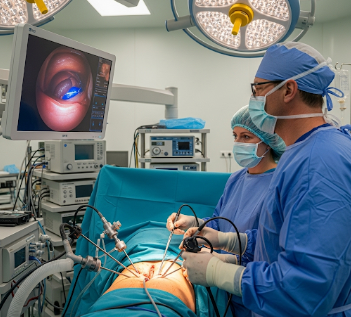
Laparoscopy, commonly called keyhole surgery, is a minimally invasive surgical technique used to examine or operate on the abdominal and pelvic organs. Instead of a large incision, the surgeon makes small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) through which a laparoscope (a thin tube with a camera and light) and specialized surgical instruments are inserted.
Key points:
- Allows diagnosis and treatment with minimal trauma.
- Used for gallbladder surgery, appendectomy, hernia repair, gynecological procedures, and fertility treatments.
- Offers faster recovery, less pain, and smaller scars compared to traditional open surgery.
- May be combined with robotic assistance in advanced surgical centers.
Why it’s done
Laparoscopy is indicated for:
- Diagnostic purposes: Evaluate abdominal pain, infertility, or internal organ abnormalities.
- Treatment of conditions: Remove the gallbladder, appendix, or ovarian cysts; repair hernias; perform hysterectomies.
- Fertility procedures: Assess and treat endometriosis, adhesions, or blocked fallopian tubes.
- Biopsies: Obtain tissue samples from abdominal or pelvic organs.
- Minimally invasive advantages: When patients require faster recovery and reduced post-operative complications.
Note: Laparoscopy is preferred when less invasive surgery is feasible, and the patient’s condition allows for safe insufflation and instrument insertion.
Alternatives
Other surgical or diagnostic approaches include:
- Open surgery (laparotomy): Traditional surgery with a large incision.
- Endoscopy: For procedures limited to the gastrointestinal tract.
- Non-surgical management: Medications, physiotherapy, or watchful waiting for some conditions.
- Ultrasound or imaging-guided interventions: For diagnostic or minor therapeutic needs.
Important: Laparoscopy is favored for its reduced pain, faster recovery, and lower risk of infection, but not all patients or conditions are suitable.
Preparation
Proper preparation is essential for safety and effectiveness:
- Medical evaluation: Blood tests, ECG, imaging studies, and anesthetic assessment.
- Fasting: Usually 6–8 hours before surgery.
- Medication review: Adjust blood thinners or other medications as instructed.
- Informed consent: Discuss procedure, risks, benefits, and possible conversion to open surgery.
- Bowel preparation: May be needed for gastrointestinal procedures.
Patient instructions:
- Wear loose, comfortable clothing and remove jewelry.
- Arrange post-operative support at home.
- Follow preoperative instructions carefully, including fasting and medication adjustments.
How it’s done
Laparoscopy is performed under general anesthesia and involves several steps:
- Small incisions: Usually 1–4 small cuts in the abdominal or pelvic region.
- Gas insufflation: Carbon dioxide is introduced to inflate the abdomen, creating space for visualization.
- Insertion of laparoscope and instruments: Camera provides a magnified view on a monitor, guiding precise instrument movements.
- Surgical procedure: The surgeon performs the necessary operation, such as removal of diseased tissue, organ repair, or biopsy.
- Closure: Instruments are removed, gas is released, and incisions are closed with sutures or surgical glue.
Duration: Typically 30 minutes to 3 hours, depending on the complexity.
Recovery
Recovery from laparoscopy is generally faster than open surgery:
- Hospital stay: Many procedures are outpatient or 1–2 days; more complex surgeries may require longer stays.
- Pain management: Mild abdominal discomfort or shoulder tip pain from gas may occur; controlled with medications.
- Return to activity: Light activities may resume within 1–2 days, with full recovery in 2–6 weeks depending on the procedure.
- Follow-up: Clinic visits ensure wound healing, absence of infection, and proper organ function.
Benefits of recovery:
- Minimal scarring and reduced post-operative pain.
- Lower risk of infection compared to open surgery.
- Faster return to daily activities and work.
Complications / Risks
Although generally safe, laparoscopy carries some risks:
- Bleeding: Minor, occasionally requiring further intervention.
- Infection: Rare at incision sites or internally.
- Organ injury: Rare but possible to the bowel, bladder, or blood vessels.
- Gas-related discomfort: Shoulder pain or bloating.
- Anesthesia risks: Standard risks of general anesthesia.
Prevention:
- Surgery performed by experienced laparoscopic surgeons.
- Strict sterile techniques and proper patient selection.
- Postoperative monitoring and early intervention for complications.
Treatment Options in Korea
Laparoscopy is widely available in Korean hospitals and specialized surgical centers:
Key features:
- State-of-the-art facilities offering diagnostic and therapeutic laparoscopy.
- Used in general surgery, gynecology, urology, and bariatric surgery.
- Advanced options include robot-assisted laparoscopy for precision procedures.
- Experienced surgeons provide preoperative counseling, minimally invasive surgery, and structured postoperative rehabilitation.
- Suitable for patients seeking reduced recovery time, smaller scars, and high-quality surgical outcomes.
Summary: Laparoscopy (keyhole surgery) in Korea is a safe, effective, and minimally invasive surgical technique. With skilled surgeons, modern equipment, and comprehensive care, patients benefit from faster recovery, reduced pain, and excellent clinical outcomes across a wide range of abdominal and pelvic conditions.