What it is
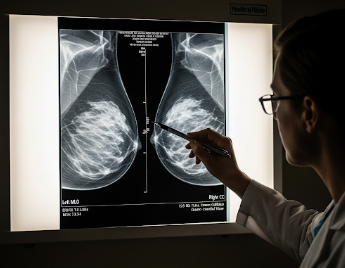
A mammogram is an X-ray imaging test of the breast used to detect early signs of breast cancer or other abnormalities. It is the most effective tool for screening women who may have no symptoms, allowing for early diagnosis and treatment.
Key points:
- Uses low-dose X-rays to create detailed images of breast tissue.
- Can identify tumors, calcifications, or other tissue changes.
- Often part of routine screening programs for women over a certain age or with risk factors.
- Helps reduce breast cancer mortality through early detection.
Why it’s done
Breast screening with mammography is recommended to:
- Detect breast cancer early: Even before lumps are noticeable.
- Monitor high-risk individuals: Women with family history, genetic mutations (BRCA1/2), or previous breast conditions.
- Assess breast changes: Lumps, nipple discharge, or skin dimpling.
- Guide further investigation: If abnormalities are detected, follow-up imaging or biopsy may be required.
Note: Screening is most effective for women aged 40–74, but the age range may vary based on guidelines and personal risk factors.
Alternatives
Other screening or diagnostic options include:
- Breast ultrasound: Often used for dense breast tissue or follow-up of mammogram findings.
- Breast MRI: Recommended for high-risk patients or those with implants.
- Clinical breast examination: Performed by a healthcare professional to detect lumps or irregularities.
- Self-breast examination: Helps individuals notice changes early but does not replace imaging.
Important: Mammography remains the gold standard for routine breast cancer screening.
Preparation
Proper preparation ensures accurate results and patient comfort:
- Schedule timing: Avoid mammograms during menstrual cycle days when breasts are tender.
- Clothing: Wear a two-piece outfit for easier access.
- Avoid deodorants or powders: Metal particles can interfere with X-ray images.
- Medical history: Inform the technician of previous breast surgeries, implants, or family history of cancer.
Patient instructions:
- Relax during the procedure to reduce discomfort.
- Bring previous mammograms for comparison if available.
- Report any breast symptoms before imaging begins.
How it’s done
Mammography is performed using specialized imaging equipment:
- Positioning: The breast is placed on the X-ray platform.
- Compression: A paddle gently compresses the breast to spread tissue for a clearer image.
- Imaging: X-rays are taken from different angles.
- Duration: Typically 10–20 minutes for both breasts.
- Analysis: Radiologists examine the images for masses, calcifications, or structural changes.
Note: Compression may cause mild discomfort, but it is brief and necessary for accurate imaging.
Recovery / Post-Procedure Considerations
Mammography is non-invasive and requires no recovery time:
- Normal activities can resume immediately.
- Mild tenderness may occur due to breast compression.
- Follow-up appointments may be needed if abnormalities are detected.
- Routine screening schedule: Typically every 1–2 years, depending on age and risk factors.
Benefits:
- Early detection of breast cancer significantly improves treatment outcomes.
- Helps monitor breast health over time.
- Enables prompt intervention for detected abnormalities.
Complications / Risks
Mammography is generally safe with minimal risk:
- Radiation exposure: Very low; considered safe for routine screening.
- False positives: May lead to unnecessary tests or anxiety.
- False negatives: Small tumors may occasionally be missed.
- Mild discomfort: Due to breast compression during imaging.
Prevention / Mitigation:
- Performed by trained radiology technicians.
- Modern equipment minimizes radiation exposure.
- Follow-up imaging or biopsy ensures accurate diagnosis when abnormalities are detected.
Treatment Options in Korea
Breast screening with mammography is widely available in hospitals, specialized imaging centers, and public health programs across Korea:
Key features:
- State-of-the-art digital and 3D mammography technology.
- Programs for high-risk individuals and routine age-based screening.
- Experienced radiologists provide accurate interpretation and timely reporting.
- Follow-up care includes ultrasound, MRI, biopsy, or referral to oncology if needed.
- Supports preventive care and early detection, improving survival rates.
Summary: Breast screening (mammogram) in Korea is a safe, effective, and essential tool for early detection of breast cancer. With advanced technology, expert radiologists, and comprehensive follow-up care, patients benefit from improved diagnostic accuracy, timely treatment, and better long-term outcomes.