Overview
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is one of the most common chronic conditions in Korea, affecting a large portion of the adult population. It is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. With Korea’s advanced medical system, early detection, lifestyle programs, and modern treatment options are widely accessible, especially through national health screening programs.
What is High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)?
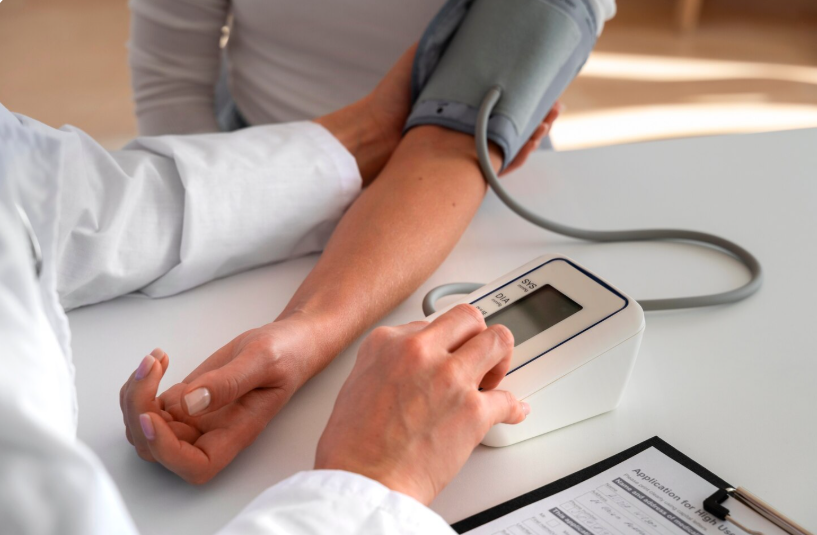
Hypertension is a condition in which the force of blood against artery walls is consistently too high, usually defined as 140/90 mmHg or above. In Korea, hypertension is considered a significant public health issue due to its strong association with cardiovascular diseases and the aging population.
Symptoms
Hypertension is often called the “silent killer” because many people show no symptoms. However, in some cases, symptoms may include:
- Persistent headaches
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
Causes
- Genetic predisposition
- Unhealthy diet (high salt intake, which is common in traditional Korean foods like kimchi and soups)
- Lack of physical activity
- Obesity
- Stress
- Aging
- Underlying conditions such as kidney disease or hormonal disorders
Risk Factors
- Age over 40
- Family history of hypertension
- High-salt diet (frequent in Korean cuisine)
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
- Obesity or central obesity
- Diabetes
- Sedentary lifestyle
Complications
If untreated, hypertension can cause:
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- Kidney damage (chronic kidney disease)
- Vision problems (hypertensive retinopathy)
- Aneurysm
Prevention
- Reducing salt intake (low-sodium kimchi and soups are promoted in Korea)
- Regular physical activity such as walking, cycling, or jogging
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding smoking
- Stress management through meditation, yoga, or counseling
- Regular health screenings (widely available through Korea’s National Health Insurance Service)
Treatment Options in Korea
Korea has advanced and comprehensive care for hypertension, focusing on both medical management and lifestyle changes:
- Diagnosis:
- Routine blood pressure measurement during national health screenings
- 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in specialized centers such as Seoul National University Hospital and Samsung Medical Center.
- Medical treatment:
- Antihypertensive medications such as ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and diuretics.
- Personalized medication plans depending on patient profile and comorbidities.
- Lifestyle modification programs:
- Dietary counseling (low-salt, DASH diet adapted for Korean meals)
- Exercise programs in hospitals and community centers
- Weight management and stress-reduction therapies
- Advanced care:
- Patients with resistant hypertension are referred to cardiovascular specialists at major hospitals like Asan Medical Center and Yonsei Severance Hospital.
- Continuous monitoring through digital health apps and telemedicine is increasingly offered.
Korea’s emphasis on early detection, combined with advanced hospital facilities and national health initiatives, makes it one of the leading countries in hypertension management.